AI-generated music: copyright and ownership issues are rapidly transforming the music industry. The rise of sophisticated algorithms capable of composing original music raises complex questions about authorship, ownership, and the very definition of artistic creation. This exploration delves into the legal, ethical, and economic implications of this technological advancement, examining the current legal landscape and proposing potential solutions for navigating this uncharted territory.
From analyzing existing copyright frameworks to exploring novel ownership models, we’ll unpack the challenges faced by artists, developers, and the music industry as a whole. We’ll consider the ethical dilemmas surrounding AI-generated music, including concerns about plagiarism and the potential displacement of human artists. Ultimately, this discussion aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted issues surrounding AI-generated music and its impact on the future of music.
Defining AI-Generated Music

AI-generated music represents a burgeoning field where artificial intelligence algorithms create musical compositions, arrangements, and soundscapes. This technology leverages computational power to automate aspects of music creation, offering new possibilities for composers, musicians, and music enthusiasts alike. The process moves beyond simple MIDI sequencing and delves into complex compositional techniques, mimicking human creativity in surprising ways.AI-generated music relies on sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to produce musical output.
These systems learn from vast datasets of existing music, analyzing patterns, structures, and stylistic elements. This learning process allows the AI to generate new music that exhibits characteristics similar to the training data, while also introducing elements of novelty and originality. The level of human intervention can vary widely, from providing only basic parameters to actively guiding the AI’s creative process.
Methods of AI Music Generation
Several methods are employed to create AI-generated music. These include rule-based systems, which use predefined musical rules and constraints to guide the composition process; Markov chains, which predict the next musical event based on probabilities derived from the training data; and deep learning models, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs), which learn complex patterns and generate highly creative and nuanced musical pieces.
The choice of method often depends on the desired level of control and the complexity of the musical style being generated.
The Role of Algorithms and Machine Learning
Algorithms are the core of AI music generation. They process vast amounts of musical data, identifying patterns, harmonies, melodies, and rhythms. Machine learning allows these algorithms to learn from this data, improving their ability to generate music that aligns with specific styles or user preferences. Different machine learning models, such as RNNs known for their sequential processing capabilities and GANs adept at generating novel and diverse outputs, are employed depending on the desired characteristics of the generated music.
For instance, RNNs might excel at generating continuous melodies, while GANs could be better suited for creating variations on a theme.
Examples of AI-Generated Music
AI-generated music spans a wide range of styles and genres. Simple examples might include background music for video games or ambient soundscapes, generated using relatively straightforward algorithms. More sophisticated examples include complex orchestral pieces, pop songs, and even experimental electronic music, often generated using deep learning models capable of capturing intricate musical nuances. The unique characteristics of AI-generated music can include unexpected harmonic progressions, novel rhythmic patterns, and textures not typically found in human-composed music.
Some AI systems even allow users to specify parameters like tempo, key, and instrumentation, providing a degree of customization.
Comparison of AI Music Generation Software
| Software | Features | Limitations | Style Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amper Music | User-friendly interface, customizable parameters, various styles | Limited creative control in some modes, potential for repetitive output | Broad range, including background music and jingles |
| Jukebox (OpenAI) | Generates music in various styles, high-quality output | Requires significant computational resources, less user-friendly interface | Diverse genres, including pop, country, and hip-hop |
| AIVA | Creates music for film, games, and advertising, various styles | May require a subscription for full functionality | Film scores, game soundtracks, and commercial music |
| Soundful | Focuses on royalty-free music creation, easy to use | Potentially less creative output compared to more advanced tools | Background music and royalty-free tracks |
Copyright Law and AI Music
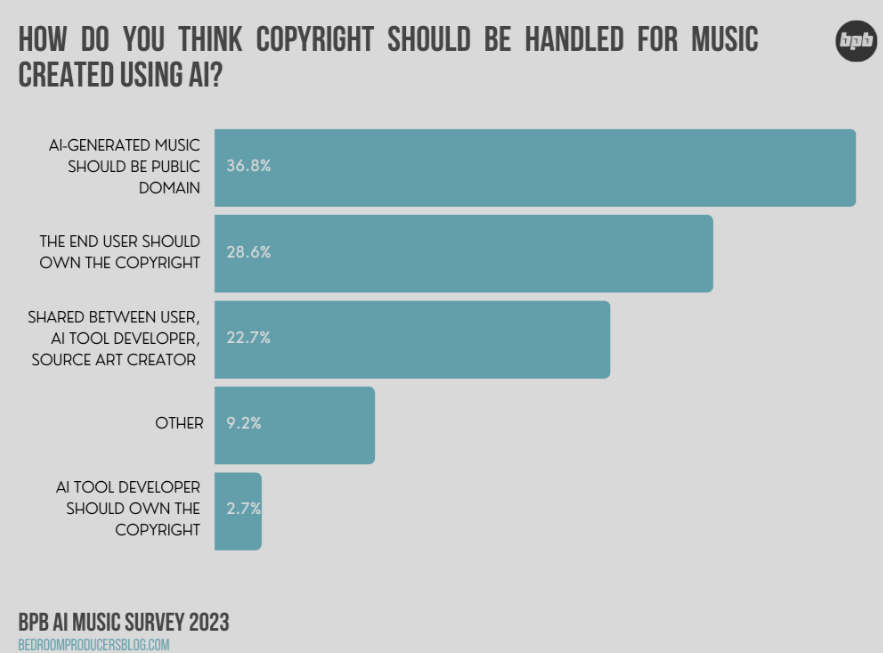
The burgeoning field of AI-generated music presents significant challenges to existing copyright law frameworks. While traditional copyright protects the expression of an idea, not the idea itself, determining authorship and ownership when an algorithm creates the music becomes complex and necessitates a re-evaluation of established legal principles. This section explores the current legal landscape and its shortcomings in addressing the unique issues raised by AI-generated musical works.The application of existing copyright laws to AI-generated music is fraught with difficulties.
Current copyright legislation generally requires human authorship for a work to be protected. This fundamental premise is challenged when the creative process is driven by an AI system, leaving questions about who—if anyone—holds the copyright. Furthermore, the nature of AI’s creative process, often involving machine learning from vast datasets of existing copyrighted material, raises concerns about potential infringement and the scope of fair use defenses.
The lack of clear legal precedent makes it difficult for artists, developers, and platforms to navigate the legal complexities surrounding the use and distribution of AI-generated music.
Authorship and Ownership in AI-Generated Music
Determining authorship and ownership is a central challenge. In the traditional sense, the author is the individual who conceived and executed the work. With AI, however, the creative process is distributed between the human programmer who designs the algorithm and the AI itself. Different legal systems might attribute authorship differently: some might favor the programmer, viewing the AI as a tool; others might argue for a shared authorship or even a unique form of AI-authorship.
The ownership of the copyright might similarly rest with the programmer, the AI’s owner, or be subject to contractual agreements. The absence of a globally unified approach to this issue creates uncertainty and potential legal disputes.
Differing Legal Interpretations of AI Music Copyright
Several legal opinions and interpretations regarding AI-generated music copyright exist, reflecting the evolving nature of the field and the lack of established legal frameworks. Some jurisdictions might lean towards a more restrictive approach, requiring a significant level of human intervention to qualify for copyright protection. Others may adopt a more flexible approach, recognizing the potential for AI to generate original and creative works deserving of copyright protection, even with minimal human input.
These differing interpretations create a fragmented legal landscape, making it difficult to predict the outcome of copyright disputes involving AI-generated music across different jurisdictions. For instance, a work deemed copyrightable in one country might be considered ineligible in another, creating significant challenges for international distribution and licensing. The lack of harmonization across international copyright laws further exacerbates this problem.
Ownership of AI-Generated Music

The question of who owns the copyright to AI-generated music is a complex and rapidly evolving area of law. Current copyright laws, largely designed for human creativity, struggle to adequately address the unique circumstances of AI authorship. This necessitates exploring various ownership models and developing a robust legal framework to ensure fairness and promote innovation within the music industry.The ownership of AI-generated music hinges on several factors, including the specific AI system used, the level of user input, and the existing legal precedents.
Different jurisdictions may also interpret these factors differently, leading to a patchwork of legal approaches. Understanding these complexities is crucial for navigating the legal landscape of AI music.
Scenarios of AI Music Ownership
Several scenarios regarding the ownership of AI-generated music exist. In one scenario, the developer of the AI system might claim ownership, arguing that the AI’s creative output is a direct result of their programming and algorithms. Alternatively, the user who inputs prompts or parameters into the AI could claim ownership, asserting that their creative direction shaped the final product.
A third possibility involves a shared ownership model, where both the developer and the user share rights to the music. The specific allocation of ownership rights in each scenario depends heavily on the terms of service, user agreements, and the specific functionalities of the AI music generation tool. For example, an AI that generates music based solely on pre-programmed algorithms would likely vest ownership in the developer, whereas an AI that allows significant user customization might lean towards user ownership or a shared model.
A Hypothetical Legal Framework for AI Music Ownership
A hypothetical legal framework for assigning ownership of AI-generated music could involve a tiered system based on the level of human involvement. A clear definition of “substantial human authorship” would be crucial. If human input is deemed minimal, ownership could default to the AI developer. Conversely, if the user provides substantial creative input, such as composing melodies, lyrics, or choosing specific instrumental arrangements, they would likely hold primary ownership.
Intermediate cases, where both developer and user contribute significantly, could result in shared ownership with clearly defined percentages. This framework would require precise legal definitions and criteria for determining the degree of human input, potentially incorporating factors like the complexity of the AI’s algorithms, the user’s level of technical expertise, and the degree of control exercised by the user over the creative process.
This tiered system aims to balance the interests of AI developers, who invest resources in creating the technology, and users, who provide the creative direction. This would necessitate a careful consideration of factors like the complexity of the AI’s algorithms and the user’s level of control.
Impact of Different Ownership Models on the Music Industry
Different ownership models for AI-generated music will have significant implications for the music industry. A developer-centric model could lead to consolidation of ownership in the hands of a few powerful tech companies, potentially stifling independent artists and smaller labels. Conversely, a user-centric model could empower individual creators, fostering a more diverse and decentralized music ecosystem. A shared ownership model could strike a balance, but would require robust mechanisms for fair and efficient distribution of royalties and licensing fees.
The impact on the existing music infrastructure – including publishing, licensing, and distribution – will depend heavily on the legal framework adopted. For example, a system prioritizing user ownership might require a re-evaluation of existing copyright registration and royalty collection processes. The potential for disputes and litigation surrounding ownership rights would also impact the overall efficiency and cost of the music industry.
Stakeholders Involved in the Ownership Debate
The ownership debate surrounding AI-generated music involves a diverse range of stakeholders with often competing interests. A clear understanding of these interests is vital for creating a fair and effective legal framework.
- AI Developers: They invest significant resources in developing AI music generation technology and have a vested interest in protecting their intellectual property.
- Musicians: Their livelihoods are directly impacted by changes in copyright law and the rise of AI-generated music. Concerns exist about the potential displacement of human musicians and the fair compensation for their creative contributions.
- Users/Creators: Individuals using AI tools to create music need clear guidelines regarding ownership and the extent of their creative rights.
- Music Labels and Publishers: They play a crucial role in the distribution and monetization of music and will need to adapt their business models to accommodate AI-generated music.
- Copyright Lawyers and Legal Professionals: They are essential in interpreting and applying copyright laws to the unique challenges posed by AI-generated music.
Ethical Considerations

The rise of AI-generated music presents a complex web of ethical dilemmas, challenging established notions of artistic creation, copyright, and authorship. The potential for plagiarism, the blurring of lines between human and machine creativity, and the impact on the livelihoods of human musicians all demand careful consideration. Addressing these concerns is crucial for ensuring the responsible development and use of AI music generation technology.The primary ethical concern revolves around the question of originality and plagiarism.
AI models are trained on vast datasets of existing music, raising the possibility that generated outputs might inadvertently or intentionally replicate existing works, violating copyright and diminishing the value of human artistic expression. Furthermore, the lack of conscious intent in AI-generated music raises questions about artistic merit and the very definition of “art.” Is a piece created by an algorithm truly art, or simply a sophisticated imitation?
This ambiguity challenges our understanding of creativity and its societal value.
Plagiarism and Artistic Originality in AI-Generated Music
AI music generation tools learn from existing musical works. This learning process, while essential for their functionality, carries the risk of generating music that is substantially similar to, or even directly copies, copyrighted material. For example, an AI trained on a large corpus of classical music might inadvertently produce a piece strikingly similar to a known symphony, raising serious copyright infringement concerns.
This necessitates the development of robust detection mechanisms and ethical guidelines to prevent such occurrences. Furthermore, the question of artistic originality is complicated by the lack of human intentionality. While an AI can generate novel musical sequences, the lack of a conscious artistic vision raises questions about the authenticity and value of the resulting work. The potential for AI to simply recombine existing elements without adding a unique artistic perspective poses a threat to the originality and integrity of music as an art form.
Ethical Dilemmas and Proposed Solutions, AI-generated music: copyright and ownership issues
Several ethical dilemmas arise from the use of AI-generated music. One is the potential displacement of human musicians and composers. As AI becomes more sophisticated, there is a concern that it could replace human artists in various musical roles, from composing film scores to creating popular music. This raises questions about the economic and social impact of AI on the music industry and the need for strategies to mitigate job displacement.
Another dilemma is the potential for misuse of AI-generated music. For instance, it could be used to create deepfakes of musicians’ voices or to generate music for purposes that infringe on intellectual property rights. Solutions include developing clear ethical guidelines for AI music generation, investing in retraining programs for displaced musicians, and implementing robust mechanisms to detect and prevent misuse.
Transparency in the creation process, clearly labeling AI-generated music, and fostering a collaborative approach between humans and AI could also help mitigate these risks.
Transparency in AI Music Creation
Transparency plays a crucial role in addressing the ethical concerns surrounding AI-generated music. Openly disclosing the methods and datasets used in the creation process is essential for assessing the originality and potential for plagiarism of AI-generated music. This transparency allows for scrutiny of the AI’s output and helps determine whether copyright infringement has occurred. Furthermore, transparently labeling AI-generated music allows listeners and consumers to make informed decisions about their consumption and avoid inadvertently supporting potentially unethical practices.
This builds trust and allows for a more responsible and ethical integration of AI into the music industry. A lack of transparency, conversely, can lead to distrust, legal disputes, and a devaluation of human artistic contributions.
Visual Representation of Ethical Concerns
Imagine a Venn diagram. One circle represents “Copyright Infringement,” encompassing instances of AI music directly copying existing works. Another circle represents “Artistic Originality,” encompassing the question of whether AI-generated music can be considered truly original or merely a sophisticated remix. The overlapping area represents the core ethical dilemma: where copyright infringement and the lack of originality intersect.
A third circle, “Economic Impact,” sits partially overlapping the other two, illustrating how copyright issues and the question of originality impact the livelihoods of human musicians. Arrows connect each circle to the central point labeled “Ethical Concerns in AI-Generated Music,” highlighting the interconnectedness of these issues.
Future of AI-Generated Music and Copyright

The rapid advancement of AI music generation technology presents a complex and evolving landscape for copyright law. As AI models become increasingly sophisticated, capable of creating original and commercially viable music, the existing legal frameworks designed for human authorship are being stretched to their limits. Understanding the potential trajectory of this technology and its interaction with copyright is crucial for navigating the future of the music industry.AI music generation is poised for significant advancements.
We can expect to see increasingly nuanced and expressive AI-composed music, capable of mimicking various musical styles and incorporating complex harmonic and rhythmic structures. Furthermore, the integration of AI with other technologies, such as virtual reality and interactive storytelling, will likely create new forms of musical experiences and raise further copyright challenges. For instance, imagine AI composing unique musical scores dynamically adapting to a user’s actions within a virtual environment – the copyright implications of such a system are vast and largely unexplored.
Technological Advancements and Copyright Law
The increasing sophistication of AI music generators will necessitate a reassessment of copyright law’s fundamental principles of authorship and originality. Current copyright law largely assumes a human creator. As AI models generate music with minimal human intervention, the question of who—or what—holds the copyright becomes increasingly pertinent. This may lead to the development of new legal frameworks that recognize AI as a potential “author” or establish a system of shared copyright between the AI developer and any human users who contribute to the creative process.
Examples of such legal developments could include the creation of new categories of intellectual property rights specifically designed for AI-generated works or the modification of existing laws to account for the unique characteristics of AI-generated music. Consider the case of a company developing a sophisticated AI system: determining copyright ownership for the music generated by this system could involve legal battles over the contribution of both the algorithms and the human programmers.
Economic and Social Impacts of Widespread AI-Generated Music
The widespread adoption of AI-generated music could significantly impact the music industry’s economic and social structures. On one hand, it has the potential to democratize music creation, enabling individuals without formal musical training to create and share their music. This could lead to a surge in musical output and a more diverse musical landscape. Conversely, it could also lead to job displacement for human musicians, composers, and songwriters, particularly those who work in genres easily replicated by AI.
The potential for copyright infringement on existing works also presents a major economic concern for artists and record labels. This could be mitigated by advancements in AI technology that allow for greater control over the use of copyrighted material in training datasets and generation processes. The economic impact will depend heavily on how effectively copyright laws adapt to this new reality, balancing the rights of creators with the opportunities presented by AI.
The rise of AI-generated jingles and background music already suggests a potential shift in the economic landscape.
Strategies for Resolving Copyright and Ownership Issues
Several strategies can be employed to address the complex copyright and ownership issues surrounding AI-generated music. One approach is to establish clear guidelines for determining copyright ownership based on the level of human involvement in the creative process. This could involve a tiered system, assigning different copyright ownership rights depending on whether the AI is used as a tool by a human creator or if the AI generates the music with minimal human input.
Another strategy is to develop new licensing models specifically designed for AI-generated music, enabling creators and users to legally access and utilize this music while protecting the rights of the relevant stakeholders. This could involve collaborative agreements between AI developers, music publishers, and artists, ensuring fair compensation for all parties involved. Finally, the development of robust technological solutions, such as watermarking or blockchain-based systems, could help to track the provenance of AI-generated music and prevent unauthorized use or distribution.
A successful strategy will likely require a multifaceted approach, combining legal reforms with technological innovations and collaborative agreements within the music industry.
Closing Summary: AI-generated Music: Copyright And Ownership Issues
The emergence of AI-generated music presents a unique challenge to established copyright and ownership paradigms. While the legal landscape remains uncertain, navigating the ethical considerations and developing a robust legal framework are crucial steps for fostering innovation while protecting the rights of all stakeholders. The future of music may well depend on our ability to address these complex issues proactively, ensuring a balanced ecosystem where both human creativity and technological advancements can thrive.

