AI assistance in color grading and video enhancement is revolutionizing video production. No longer confined to the realm of science fiction, artificial intelligence is rapidly becoming an indispensable tool for filmmakers, editors, and content creators alike. This transformative technology offers unprecedented speed, precision, and creative possibilities, streamlining workflows and unlocking new levels of visual artistry. From automated color correction and stylistic adjustments to advanced upscaling and noise reduction, AI is reshaping the landscape of video post-production, pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable.
This exploration delves into the intricacies of AI-powered video editing, examining the algorithms, techniques, and practical applications that are driving this exciting evolution. We’ll compare AI-assisted workflows with traditional methods, analyze real-world case studies, and consider the ethical implications of this increasingly powerful technology. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of AI’s role in the future of video production and its impact on the creative process.
Introduction to AI in Color Grading and Video Enhancement
The video editing landscape is undergoing a significant transformation thanks to the integration of artificial intelligence. AI-powered tools are rapidly becoming indispensable for professionals and enthusiasts alike, offering unprecedented capabilities in color grading and video enhancement. These tools automate complex tasks, improve efficiency, and often deliver results surpassing those achievable through traditional methods.AI’s impact on color grading and video enhancement stems from its ability to analyze vast amounts of visual data and identify patterns that would be impossible for a human to discern in a reasonable timeframe.
This allows for highly precise and consistent adjustments across entire projects, leading to a more streamlined and efficient workflow. Furthermore, AI can address challenges that previously required significant manual effort or specialized skills, making high-quality video production more accessible.
AI Algorithms in Color Grading and Video Enhancement
Several different AI algorithms are employed in color grading and video enhancement applications. These algorithms leverage techniques from machine learning and deep learning to achieve impressive results. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), for example, are commonly used for tasks such as upscaling video resolution, noise reduction, and detail enhancement. These networks excel at identifying and processing spatial patterns within images and video frames.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are often utilized for tasks requiring temporal consistency, such as stabilizing shaky footage or generating smooth slow-motion effects. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are also employed; these networks consist of two competing neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – that work together to produce highly realistic and natural-looking enhancements, for example, by intelligently filling in missing details or improving the overall aesthetic quality of a video.
Specific examples of algorithms include those developed by companies like Topaz Labs (Gigapixel AI, Video Enhance AI), Adobe (Sensei AI), and others, each employing proprietary techniques based on these fundamental approaches.
Benefits of AI-Powered Color Grading and Video Enhancement
Compared to traditional methods, AI-powered tools offer several key advantages. First, they significantly reduce the time and effort required for color grading and enhancement. Tasks that previously demanded hours of manual work can now be completed in minutes, allowing editors to focus on creative aspects rather than tedious adjustments. Second, AI algorithms often produce more consistent and accurate results.
They can identify subtle imperfections and inconsistencies that are easily missed by the human eye, leading to a higher overall quality. Third, AI tools can handle large volumes of data with ease, making them ideal for processing extensive video projects. Finally, AI-powered tools democratize access to professional-grade video editing capabilities. Features previously available only to highly skilled professionals are now accessible to a wider range of users, fostering creativity and innovation.
For instance, tools that previously required expertise in color science can now be used effectively with user-friendly interfaces, making advanced techniques accessible to amateur videographers.
AI-Driven Color Grading Techniques
AI is revolutionizing the post-production workflow, significantly impacting color grading. Previously a painstaking manual process, color correction and stylistic adjustments are now increasingly automated, leading to faster turnaround times and potentially more consistent results. This section details the process of AI-assisted color grading, compares it to traditional methods, and analyzes its strengths and weaknesses.AI-assisted color grading leverages machine learning algorithms trained on vast datasets of images and videos.
These algorithms can identify and correct various color imperfections, such as white balance issues, color casts, and inconsistencies in exposure. Beyond simple correction, AI can also apply sophisticated stylistic adjustments, mimicking the look of specific film stocks, creating specific moods, or matching the color palette of a reference image. The process typically involves uploading footage to a software application incorporating AI, selecting a desired effect or preset, and then allowing the AI to process the video.
Users can then fine-tune the results manually, retaining creative control while leveraging the speed and efficiency of AI.
Automated Color Correction
AI algorithms excel at automating tedious color correction tasks. They can quickly analyze footage, identifying and correcting issues such as uneven exposure, color casts (e.g., a bluish tint in shadows), and white balance problems. This automation dramatically reduces the time spent on initial color correction, allowing colorists to focus on more creative aspects of the process. For example, an AI system might automatically detect and correct a green color cast caused by shooting under artificial light, saving hours of manual adjustment.
The AI can also identify and correct color fringing or chromatic aberration, artifacts that are difficult and time-consuming to fix manually.
Stylistic Adjustments with AI
Beyond basic correction, AI can apply sophisticated stylistic adjustments. This can involve mimicking the look of specific film stocks (e.g., Kodak Vision3 500T), applying specific color grading “looks” (e.g., a desaturated, vintage aesthetic), or even matching the color palette of a reference image. This allows for consistent branding across multiple projects or the creation of unique stylistic choices that would be extremely time-consuming to achieve manually.
Imagine creating a consistent, desaturated look for a series of commercials – AI can quickly apply this look across all footage, ensuring visual unity.
Comparison of AI and Manual Color Grading
The following table compares AI and manual color grading techniques across key aspects:
| Feature | AI Color Grading | Manual Color Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Significantly faster, especially for basic corrections | Can be very time-consuming, particularly for large projects |
| Accuracy | High accuracy for basic corrections; stylistic accuracy depends on the algorithm and training data | High accuracy achievable with skilled colorists, but prone to human error |
| Creative Control | Limited creative control in fully automated modes; significant control when used as a starting point for manual adjustments | Complete creative control, but requires extensive expertise |
| Cost | Potentially lower labor costs, but requires software investment | High labor costs, especially for complex projects |
AI-Powered Video Enhancement Methods
AI is revolutionizing video enhancement, offering unprecedented capabilities to improve video quality across various aspects. These advancements leverage sophisticated algorithms and neural network architectures to tackle challenges like low resolution, noise, and artifacts, resulting in significantly clearer and more visually appealing videos. This section delves into the core methods employed in AI-powered video enhancement.AI algorithms for video enhancement employ a range of techniques to address specific issues.
Upscaling algorithms increase the resolution of low-resolution videos, while noise reduction algorithms minimize grain and visual imperfections. Artifact removal focuses on eliminating compression artifacts and other visual distortions. These algorithms often work in concert to deliver a comprehensive enhancement.
Upscaling Algorithms
Upscaling algorithms aim to increase the resolution of videos without introducing significant artifacts or blurring. Super-resolution convolutional neural networks (SRCNNs) are commonly used, learning intricate mappings between low-resolution and high-resolution image patches. These networks analyze the low-resolution input and generate a higher-resolution output by learning complex relationships between pixels. Examples include EDSR (Enhanced Deep Super-Resolution) and RDN (Residual Dense Network), which have demonstrated impressive results in upscaling various video formats.
These algorithms often incorporate techniques like residual learning and dense connections to improve accuracy and efficiency.
Noise Reduction Algorithms
Noise in videos can stem from various sources, including low-light conditions, sensor limitations, and compression artifacts. AI-powered noise reduction techniques effectively mitigate this issue. Many approaches leverage deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), to learn and remove noise while preserving fine details. These networks are trained on extensive datasets of noisy and clean videos, learning to distinguish between noise and actual video content.
The effectiveness of these algorithms often depends on the type and level of noise present in the video. For example, a denoising autoencoder could be used to learn a compressed representation of the clean video, effectively separating noise from the original signal.
Artifact Removal Algorithms
Video compression often introduces artifacts, such as blocking, ringing, and mosquito noise. AI algorithms are employed to effectively remove or reduce the visibility of these artifacts. These algorithms typically use deep learning models trained on videos with and without artifacts. The networks learn to identify and remove these artifacts while preserving the original video content. For instance, a generative adversarial network (GAN) could be trained to generate clean video frames, effectively removing artifacts without introducing new distortions.
The discriminator in the GAN would learn to differentiate between real and generated frames, driving the generator to produce increasingly realistic artifact-free outputs.
Neural Networks for Video Enhancement
Several types of neural networks are used for video enhancement. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are prevalent due to their ability to capture spatial relationships between pixels. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), particularly LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory networks), excel at processing sequential data like video frames, considering temporal dependencies. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) offer powerful methods for generating high-quality enhanced videos by pitting a generator network against a discriminator network.
Each network type offers unique advantages depending on the specific enhancement task and desired outcome.
AI-Driven Video Enhancement Flowchart
A simplified flowchart illustrating the process would look like this:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would start with “Input Video,” branching to “Preprocessing” (e.g., frame extraction, format conversion). Preprocessing would lead to “AI Model Application” (e.g., upscaling, denoising, artifact removal using specified neural networks). “AI Model Application” would then lead to “Post-processing” (e.g., frame merging, format conversion).
Finally, “Post-processing” would lead to “Output Enhanced Video.”] The flowchart visually depicts the sequential steps involved: input video, preprocessing steps to prepare the video for AI processing, application of the chosen AI model(s) for enhancement, post-processing to refine the results, and finally the output of the enhanced video. Different models could be applied in parallel or sequentially, depending on the specific enhancement requirements.
Case Studies
AI is rapidly transforming professional video production workflows, impacting film, television, and advertising. Its applications range from streamlining tedious tasks to enabling creative possibilities previously unimaginable. This section examines real-world examples of AI’s integration into professional video editing, highlighting both its successes and limitations.
AI in Film Production
The use of AI in film production is growing, with applications in various stages of the workflow. For instance, AI-powered tools are used for automated scene detection and organization, significantly reducing the time spent on manual logging and reviewing footage. Furthermore, AI algorithms can assist in creating realistic visual effects, such as crowd simulation and digital cleanup of imperfections, freeing up artists to focus on more complex tasks.
Major studios are increasingly incorporating AI for tasks such as upscaling older film footage to higher resolutions, improving its overall visual quality for modern releases and archival purposes. A notable example is the restoration of classic films, where AI algorithms can intelligently remove scratches, grain, and other artifacts while preserving the original artistic intent.
AI in Television Production
Television production benefits from AI’s efficiency gains, particularly in post-production. AI-powered color grading tools can analyze footage and automatically suggest color palettes and adjustments, speeding up the process and ensuring consistency across episodes. Automated transcription and translation services, powered by AI, streamline subtitle creation and localization efforts, making content accessible to a wider global audience. In live broadcasting, AI can be used for real-time quality control, detecting and correcting issues such as dropped frames or audio glitches.
Furthermore, AI-driven analysis of audience viewing habits can inform programming decisions, helping broadcasters tailor their content to viewer preferences.
AI in Advertising Video Production, AI assistance in color grading and video enhancement
AI’s impact on advertising is significant, enabling faster turnaround times and more targeted campaigns. AI-powered tools can automatically generate variations of advertisements, testing different creative elements and messaging to optimize campaign performance. This includes analyzing viewer response to determine which versions resonate most effectively, ultimately leading to higher ROI. Furthermore, AI can assist in creating personalized ad experiences, tailoring messaging and visuals to individual viewer profiles based on their online behavior and preferences.
This level of customization enhances engagement and effectiveness compared to traditional, generalized advertising approaches.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Professional Video Production
While AI offers significant advantages, challenges remain. The high computational cost of running complex AI algorithms can be prohibitive for smaller production houses. Furthermore, the accuracy of AI-driven tools is not always perfect, requiring human oversight and correction. Concerns about bias in AI algorithms, particularly in areas such as facial recognition and object detection, must also be addressed to ensure fairness and avoid perpetuating stereotypes.
The “black box” nature of some AI systems can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at their results, hindering trust and collaboration between human editors and AI tools. Finally, the integration of AI into existing workflows requires significant training and adaptation for professionals accustomed to traditional methods.
Comparison of Professional Video Editing Software with AI Capabilities
The adoption of AI in professional video editing software is rapidly evolving. Below is a comparison of several leading packages, focusing on their AI capabilities. Note that features and capabilities are subject to change based on software updates.
| Software | AI-Powered Color Grading | AI-Powered Video Enhancement | Other AI Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Premiere Pro | Sensei-powered features for automated color correction and style matching | AI-assisted upscaling and noise reduction | Automated transcription, facial recognition, object tracking |
| DaVinci Resolve | Powerful AI-powered color matching and grading tools | AI-based noise reduction and upscaling | AI-assisted editing suggestions, scene detection |
| Final Cut Pro | Machine learning-powered color correction and grading assistance | Improved noise reduction and stabilization | Automated background removal, improved audio cleanup |
| Avid Media Composer | AI-assisted color correction and grading | AI-powered noise reduction and upscaling | Improved audio restoration, advanced metadata management |
Future Trends and Developments in AI Video Enhancement: AI Assistance In Color Grading And Video Enhancement
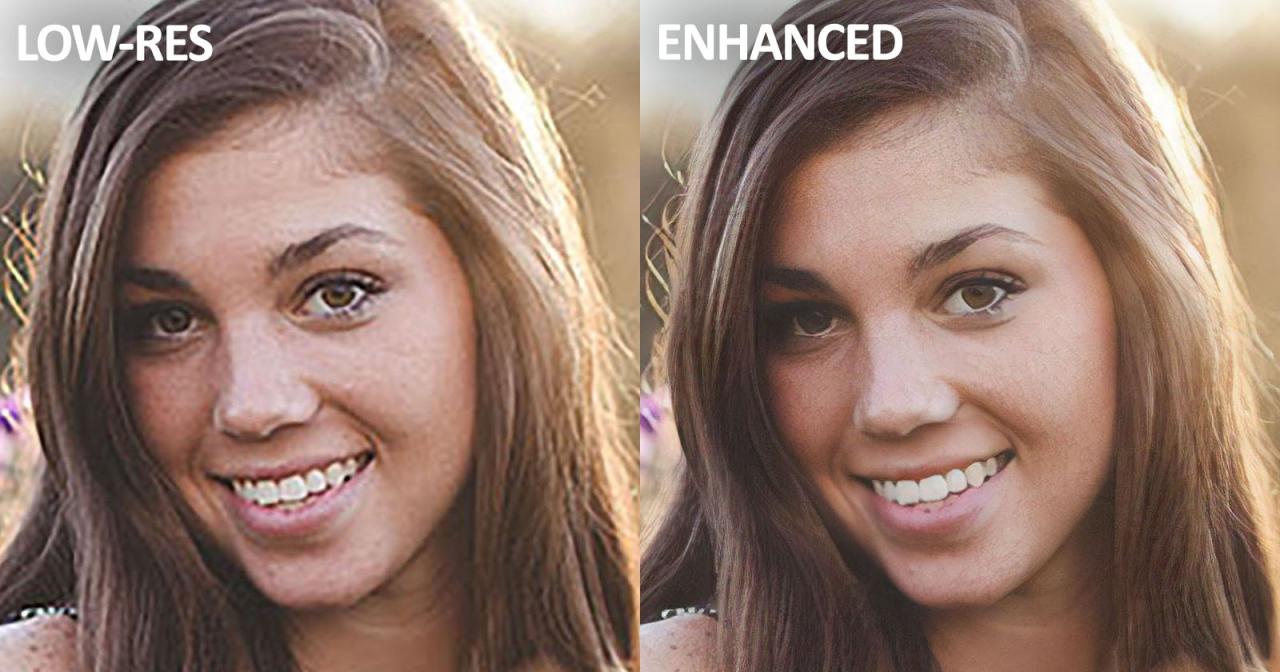

The intersection of artificial intelligence and video editing is rapidly evolving, promising a future where the creation and manipulation of video content become significantly more accessible and efficient. AI’s role will extend beyond simple automation, moving towards intelligent assistance and creative augmentation, fundamentally altering the video editing workflow. Advancements in deep learning and computer vision are the key drivers behind this transformation.AI’s influence on color grading and video enhancement will become increasingly sophisticated.
We can expect more nuanced and context-aware algorithms capable of understanding not just the technical aspects of a video, but also its artistic intent. This will allow for more intuitive and powerful tools that empower both novice and expert users alike.
Enhanced Real-Time Processing Capabilities
The future will see a dramatic increase in the speed and efficiency of AI-powered video enhancement. Current limitations in processing power and computational resources are gradually being overcome through advancements in hardware and software optimization. Real-time AI-assisted color grading and upscaling will become the norm, enabling seamless integration into live streaming workflows and even facilitating interactive video editing experiences.
Imagine a live broadcast where AI automatically adjusts color balance and sharpness based on changing lighting conditions, all without any manual intervention. This real-time processing will become crucial for applications like live sports broadcasting, virtual events, and remote video conferencing.
AI-Driven Generative Video Editing
Deep learning models are rapidly advancing in their ability to generate novel video content. This opens up exciting possibilities for AI-assisted video editing, where the AI can intelligently suggest edits, create transitions, or even generate entirely new video sequences based on user input or analysis of existing footage. For example, an AI could automatically generate a stylized slow-motion sequence from a standard-speed clip, or create a seamless transition between two disparate scenes by generating intermediate frames.
This capability is particularly useful for content creators who lack the time or expertise to manually create complex effects. Consider a film editor using an AI to generate several versions of a fight scene with different camera angles and action sequences, all based on a single, original take. The AI could analyze the original footage, identify key moments and actions, and then synthesize variations, drastically reducing the time and resources needed for post-production.
Hyper-Realistic Upscaling and Restoration
AI-powered upscaling techniques are constantly improving, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of resolution enhancement. Future algorithms will be capable of generating incredibly realistic high-resolution video from low-resolution source material, effectively eliminating the limitations of older recordings. Moreover, AI will play a significant role in video restoration, automatically removing artifacts, noise, and scratches from damaged footage, preserving historical recordings and valuable family memories.
Imagine restoring a grainy, low-resolution home movie from the 1950s to a crisp, high-definition version, with colors enhanced and artifacts removed automatically. This technology will be invaluable for archiving and preserving precious video content.
Hypothetical Future Video Editing Tool: “Aether”
Aether is a hypothetical future video editing tool that seamlessly integrates advanced AI capabilities. This software uses a multi-modal AI system that understands both the technical and artistic aspects of video. Aether’s interface is intuitive and user-friendly, offering a range of AI-powered tools. It can automatically color grade footage, optimizing for various styles and moods, while also offering granular control for fine-tuning the results.
Aether can intelligently upsample low-resolution video to 8K resolution, seamlessly removing artifacts and enhancing details. It can also automatically generate creative transitions, suggesting and creating options based on the content and context of the video. Further, Aether provides advanced AI-powered tools for video restoration, automatically removing noise, scratches, and other imperfections. The system learns from the user’s editing style and preferences, offering personalized recommendations and automating repetitive tasks.
Finally, Aether incorporates a generative video editing capability, allowing users to create variations of scenes or even generate entirely new footage based on the existing material.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Video Editing
The increasing sophistication of AI in video editing raises crucial ethical questions. While AI offers unprecedented capabilities for color grading and enhancement, its deployment necessitates careful consideration of potential biases, transparency issues, and the impact on the workforce. Failing to address these concerns risks exacerbating existing inequalities and undermining the integrity of the video editing profession.AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets of video footage, and these datasets often reflect existing societal biases.
For example, an algorithm trained primarily on footage featuring light-skinned individuals might produce color grades that are less accurate or flattering for individuals with darker skin tones. Similarly, enhancement algorithms might inadvertently amplify existing stereotypes present in the training data, leading to skewed or unfair representations. This bias isn’t necessarily intentional; it’s a consequence of the data used to train the AI.
The lack of diversity in training datasets can lead to biased outputs, perpetuating harmful stereotypes and inequities.
Bias in AI Algorithms
The presence of bias in AI algorithms used for color grading and video enhancement is a significant concern. These biases can manifest in several ways, including skewed color palettes that favor certain skin tones or features, and the disproportionate enhancement or suppression of certain elements within a video based on pre-existing biases in the training data. For instance, an algorithm trained predominantly on Western cinema might subtly alter the color grading of a film from a different cultural context, imposing a Western aesthetic that misrepresents the original artistic intent.
Addressing this requires careful curation of training datasets to ensure representation from diverse sources and cultures, along with ongoing monitoring and auditing of algorithm outputs for bias. Techniques like adversarial training can help mitigate these biases, but vigilance remains crucial.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are paramount in the use of AI-powered video editing tools. Users should be aware of the algorithms employed, their limitations, and the potential for bias. This requires clear labeling and documentation of the AI tools, enabling informed decision-making and facilitating critical evaluation of the outputs. Furthermore, developers bear a responsibility to implement mechanisms for identifying and mitigating biases, and to provide users with tools to control and adjust the AI’s influence.
A lack of transparency allows biases to go unchecked, potentially leading to the dissemination of manipulated or misleading content. Accountability mechanisms, including clear lines of responsibility for the outputs of AI-powered tools, are vital to ensuring ethical use.
Impact on Employment of Human Video Editors
The integration of AI into video editing has the potential to significantly alter the employment landscape for human video editors. While AI can automate certain tasks, freeing up human editors to focus on more creative aspects of the work, there’s also the risk of job displacement. Some roles might become obsolete as AI takes over repetitive or technically demanding tasks.
However, it is also likely that new roles will emerge, requiring skills in AI management, data analysis, and creative direction of AI-assisted workflows. The challenge lies in ensuring a just transition for the workforce, potentially through retraining programs and the development of new job roles that leverage the collaborative potential of humans and AI. The focus should be on augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them entirely.
Examples include companies already investing in upskilling their workforce to incorporate AI into their existing skillsets.
Illustrative Examples
AI-powered video enhancement tools are revolutionizing the post-production process, offering significant improvements in visual quality that were previously unattainable through traditional methods. These advancements are particularly noticeable in areas like resolution upscaling, color correction, and noise reduction. The following examples illustrate the transformative power of AI in enhancing video content.
Consider a scene from an older home movie, shot on a low-resolution camera. Before AI enhancement, the footage is grainy, with muted colors and noticeable compression artifacts. The faces of the individuals in the scene are blurry, lacking detail. The overall color palette is washed out, with a significant loss of contrast. After applying an AI enhancement algorithm, the resolution is noticeably improved.
The grain is significantly reduced, revealing finer details in clothing textures and facial features. Colors appear more vibrant and accurate, with a richer dynamic range, showcasing a more realistic representation of the original scene. The compression artifacts are largely mitigated, resulting in a cleaner and smoother visual experience. This demonstrates AI’s capability to restore lost detail and enhance the overall fidelity of the video.
Comparison of AI and Traditional Enhancement Methods
A direct comparison between AI-enhanced and traditionally enhanced video reveals the significant advantages of AI. Let’s imagine a low-light scene, initially plagued by excessive noise and a lack of sharpness. Traditional methods, such as noise reduction filters, often result in a loss of detail and a softening of the image. The color saturation might also be reduced to minimize noise, leading to a less vibrant final product.
Furthermore, these methods can introduce artifacts of their own, such as halos around edges or a blurring effect across the entire image. In contrast, an AI-enhanced version of the same scene exhibits a remarkable difference. The noise is reduced effectively without sacrificing detail; edges remain sharp, and colors retain their vibrancy. The AI algorithm intelligently distinguishes between noise and actual image data, resulting in a cleaner, sharper, and more visually appealing final product.
The enhanced video maintains a natural look, avoiding the unnatural smoothing or artificial sharpening often associated with traditional techniques. The reduction in artifacts is also markedly superior, creating a more refined and professional-looking result. This difference highlights the superior performance of AI in handling complex noise reduction and detail preservation tasks.
Wrap-Up

The integration of AI in color grading and video enhancement signifies a pivotal moment in video production. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are undeniable. From democratizing access to professional-grade tools to accelerating workflows and pushing creative boundaries, AI is empowering a new generation of visual storytellers. As AI algorithms continue to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and intuitive tools, further blurring the lines between human creativity and technological innovation.
The future of video is undeniably intelligent, and the journey has only just begun.

