How is artificial intelligence changing the way we live and work? This question increasingly defines our modern world. From the mundane to the monumental, AI’s influence is undeniable, reshaping our daily routines, transforming workplaces, and even redefining creativity itself. This exploration delves into AI’s pervasive impact, examining its benefits and challenges across various sectors, from healthcare and education to communication and entertainment.
We’ll explore how AI-powered tools streamline our lives, automating tasks and offering personalized experiences. Simultaneously, we’ll address the anxieties surrounding job displacement, algorithmic bias, and data privacy. The journey ahead is one of understanding both the transformative potential and the inherent responsibilities associated with this rapidly evolving technology.
AI’s Impact on Daily Life
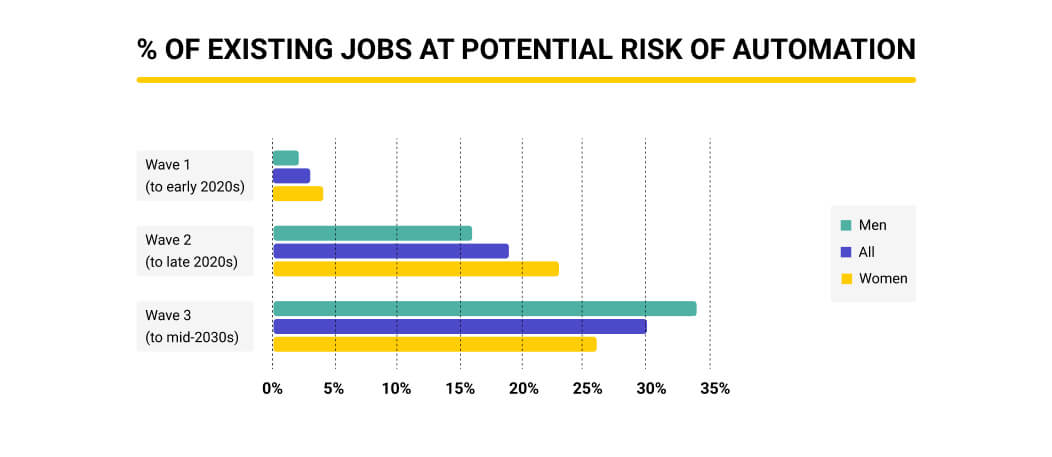
Artificial intelligence is rapidly weaving itself into the fabric of our daily lives, subtly yet profoundly altering how we interact with the world around us. From the mundane to the more complex aspects of our routines, AI’s influence is undeniable, impacting everything from how we manage our schedules to how we navigate our cities. This pervasive integration presents both opportunities and challenges, reshaping our experiences in ways we are only beginning to understand.
AI-Powered Personal Assistants and Daily Routines
AI-powered personal assistants, such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, are transforming daily routines by streamlining tasks and providing readily accessible information. These virtual assistants can set reminders, manage calendars, make calls, send messages, and control smart home devices, all through voice commands. This hands-free interaction frees up cognitive resources and allows individuals to multitask more efficiently. For example, a busy professional can dictate emails while commuting, or a parent can set timers for cooking while simultaneously attending to a child’s needs.
The convenience and efficiency offered by these assistants are reshaping how people organize and manage their time, leading to increased productivity and a smoother daily flow.
AI’s Influence on Personalized Recommendations
AI algorithms are at the heart of personalized recommendations in various platforms, including streaming services like Netflix and Spotify, and e-commerce sites like Amazon. These algorithms analyze user data, such as viewing history, purchase patterns, and ratings, to predict preferences and suggest relevant content or products. This personalized approach enhances user experience by reducing information overload and increasing the likelihood of finding engaging content or desired items.
For instance, Netflix’s recommendation engine suggests shows based on past viewing habits, while Amazon’s algorithm suggests products based on previous purchases and browsing history. This targeted approach boosts customer satisfaction and drives sales, making it a cornerstone of modern digital marketing.
AI’s Impact on Transportation and Navigation Systems, How is artificial intelligence changing the way we live and work?
AI is revolutionizing transportation and navigation through advanced features in vehicles and mapping applications. Self-driving cars, though still under development, utilize AI-powered sensors and algorithms to navigate roads, avoid obstacles, and make driving decisions. Navigation apps like Google Maps leverage AI to optimize routes based on real-time traffic conditions, providing users with the fastest and most efficient paths.
Furthermore, AI-powered predictive maintenance systems are being implemented to monitor vehicle performance and predict potential mechanical failures, ensuring safer and more reliable transportation. These advancements promise to improve traffic flow, reduce accidents, and enhance overall transportation efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI-Driven Home Automation
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Increased convenience and efficiency in managing household tasks. | High initial investment costs for installing smart home devices. |
| Enhanced home security through smart locks, security cameras, and motion sensors. | Potential privacy concerns related to data collection and usage by AI systems. |
| Energy savings through automated control of lighting, heating, and cooling systems. | Dependence on technology and potential for system malfunctions or outages. |
| Improved accessibility for individuals with disabilities through voice control and automation features. | Complexity of setting up and managing multiple interconnected devices. |
AI’s Transformation of Workplaces: How Is Artificial Intelligence Changing The Way We Live And Work?
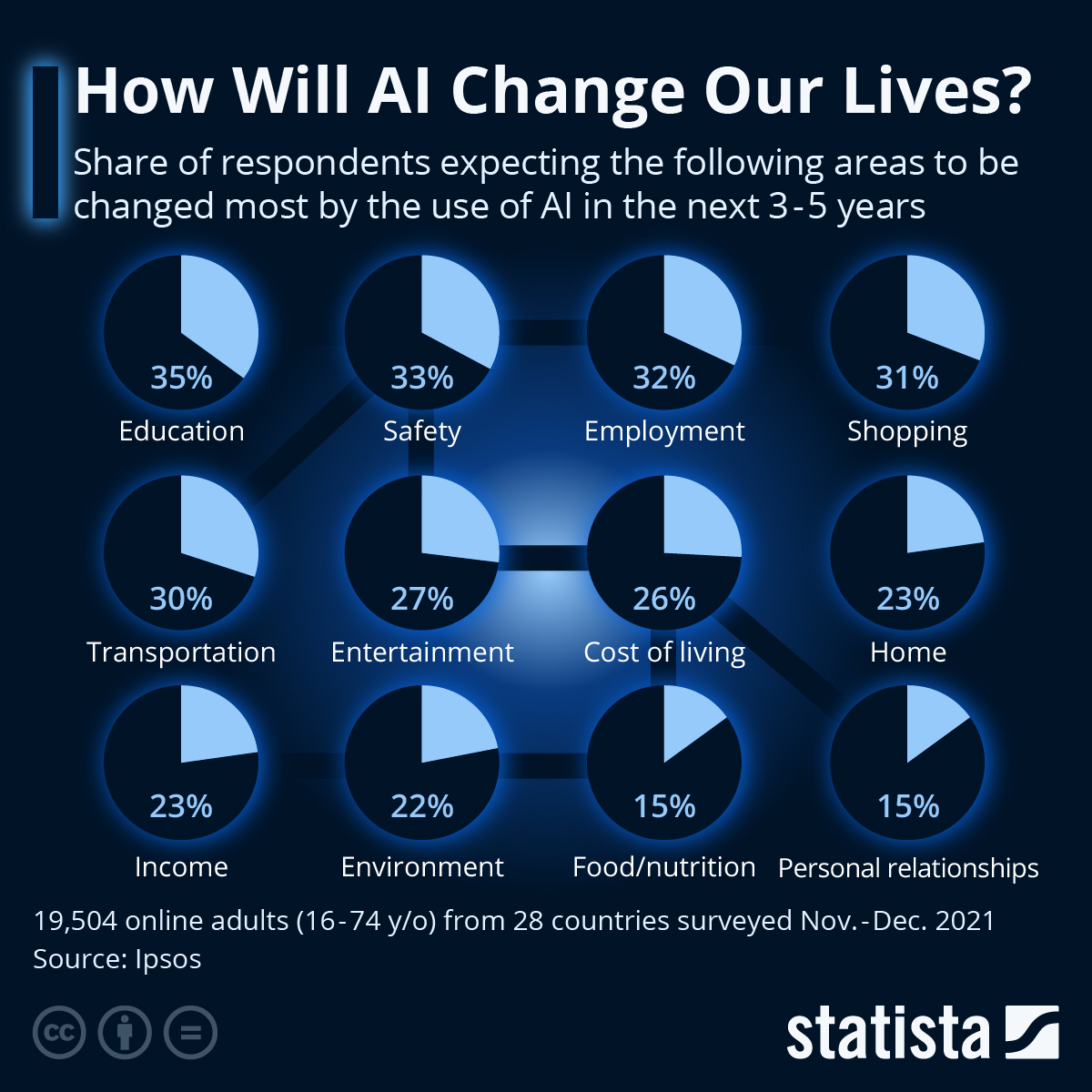
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping the landscape of work, automating tasks, altering job roles, and creating new career opportunities across numerous industries. This transformation presents both challenges and opportunities, demanding adaptation and strategic planning from businesses and individuals alike. Understanding the multifaceted impact of AI on the workplace is crucial for navigating this evolving environment.AI is automating tasks in various industries by leveraging machine learning algorithms and sophisticated software to perform repetitive, data-heavy processes more efficiently and accurately than humans.
This automation is not limited to manufacturing; it extends to sectors like finance (algorithmic trading, fraud detection), healthcare (diagnosis support, personalized medicine), and customer service (chatbots, virtual assistants). The impact varies widely depending on the industry’s reliance on routine tasks and the availability of suitable data for AI training.
Automation of Tasks Across Industries
The implementation of AI-driven automation is significantly altering workflow across various sectors. In manufacturing, robots equipped with AI are performing assembly line tasks, increasing production speed and precision while reducing human error. In the financial sector, AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify fraudulent transactions, improving security and efficiency. Customer service is increasingly relying on AI-powered chatbots to handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to address more complex issues.
The healthcare industry utilizes AI for diagnostic support, analyzing medical images and patient data to assist doctors in making informed decisions. These examples highlight the widespread adoption of AI for automation, impacting productivity and efficiency across a broad spectrum of industries.
AI’s Influence on Job Roles and Career Opportunities
AI’s influence on job roles is complex, leading to both job displacement in some areas and the creation of new roles in others. While some routine tasks are automated, new positions requiring expertise in AI development, maintenance, and ethical considerations are emerging. For instance, data scientists, AI ethicists, and AI trainers are in high demand. Existing roles are also transforming; for example, radiologists are increasingly using AI-assisted diagnostic tools, enhancing their efficiency and accuracy.
This shift requires upskilling and reskilling initiatives to equip the workforce with the necessary competencies to thrive in the AI-driven economy. The overall impact on employment rates depends heavily on the rate of technological advancement and the ability of workers to adapt to the changing job market.
AI’s Impact on Productivity and Employment Rates
The relationship between AI, productivity, and employment rates is a subject of ongoing debate. While AI undoubtedly boosts productivity by automating tasks and optimizing processes, its impact on employment rates is less clear-cut. Some studies suggest that AI will lead to net job losses in certain sectors, while others predict the creation of more jobs than are lost. The net effect depends on various factors, including the pace of technological adoption, government policies supporting retraining and reskilling, and the overall economic climate.
For example, the rise of e-commerce, fueled by AI-powered logistics and recommendation systems, has created numerous jobs in areas like warehousing and delivery, while simultaneously impacting traditional retail employment. The ultimate outcome requires careful monitoring and proactive measures to mitigate potential negative consequences.
Human-AI Collaboration in a Workplace Setting
Imagine a team of customer service representatives at a large telecommunications company. Each representative uses an AI-powered assistant that analyzes customer queries in real-time, providing relevant information and suggested solutions. The AI assistant handles simple inquiries autonomously, freeing the human representative to focus on more complex issues requiring empathy and nuanced problem-solving. The human representative retains control, overriding the AI’s suggestions when necessary and leveraging the AI’s insights to provide faster and more accurate service.
This collaborative model combines the efficiency of AI with the human touch essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and building strong relationships. The AI assistant acts as a powerful tool augmenting the human representative’s capabilities, rather than replacing them entirely.
AI and Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. From accelerating drug discovery to personalizing treatment plans, AI’s impact is profound and far-reaching, promising a future where healthcare is more efficient, effective, and accessible.AI applications in healthcare are already delivering tangible benefits, significantly impacting various aspects of medical practice and research.
The integration of AI is not merely augmenting existing processes; it’s fundamentally reshaping how healthcare is delivered and experienced.
AI in Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
AI algorithms are being used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, to detect diseases like cancer at earlier stages with greater accuracy than human radiologists alone. For example, AI-powered systems are being deployed to identify subtle anomalies in mammograms, potentially leading to earlier detection of breast cancer and improved patient outcomes. Furthermore, AI is assisting in the diagnosis of other conditions, including cardiovascular disease and diabetic retinopathy, by analyzing patient data and identifying patterns indicative of these diseases.
In treatment, AI is being used to personalize treatment plans, predict patient responses to therapy, and even assist in robotic surgery, improving precision and minimizing invasiveness.
AI’s Revolution of Drug Discovery and Development
The process of drug discovery and development is notoriously long, expensive, and often unsuccessful. AI is dramatically accelerating this process by analyzing vast datasets of molecular structures, genetic information, and clinical trial data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety. Machine learning algorithms can sift through millions of compounds, identifying those most likely to be effective against specific diseases, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with traditional drug discovery methods.
For instance, Atomwise uses AI to discover potential drug candidates, including those for the Ebola virus and the treatment of neglected tropical diseases. This significantly shortens the time required to bring life-saving medications to market.
AI in Personalized Medicine and Patient Care
AI is enabling the development of personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. AI algorithms can analyze patient data to predict the likelihood of developing certain diseases, allowing for proactive interventions and preventative measures. Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are providing patients with 24/7 access to medical information and support, improving patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
Wearable sensors and AI-powered analytics can monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, alerting healthcare providers to potential problems before they escalate. This allows for more proactive and personalized patient care.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Healthcare
The increasing use of AI in healthcare raises several important ethical considerations that require careful attention. It is crucial to address these issues proactively to ensure responsible and beneficial implementation of AI technologies.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting patient data is paramount. Robust security measures are needed to prevent unauthorized access and breaches of sensitive medical information.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms are trained on data, and if this data reflects existing societal biases, the algorithms may perpetuate or even amplify these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Transparency and Explainability: It’s crucial to understand how AI algorithms make decisions, especially in high-stakes medical contexts. Lack of transparency can erode trust and hinder accountability.
- Responsibility and Liability: Determining liability in cases of AI-related medical errors is a complex legal and ethical challenge.
- Access and Equity: Ensuring equitable access to AI-powered healthcare technologies is essential to prevent widening health disparities.
AI and Education
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the educational landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities to personalize learning, automate administrative tasks, and enhance accessibility for diverse learners. Its impact extends beyond simple technological integration; AI is fundamentally reshaping how we teach and learn.AI-powered tools are revolutionizing the educational experience, moving away from the one-size-fits-all approach towards a more personalized and adaptive model.
Personalized Learning Experiences
AI algorithms analyze student performance data, identifying individual strengths and weaknesses. This allows for the creation of customized learning pathways tailored to each student’s needs. Adaptive learning platforms adjust the difficulty and content of lessons in real-time, ensuring students are constantly challenged but not overwhelmed. For instance, a student struggling with algebra might receive additional practice problems and targeted explanations, while a student excelling in the subject could be presented with more advanced concepts.
This personalized approach fosters deeper understanding and improved learning outcomes. Furthermore, AI-powered tutoring systems provide individualized support, answering questions and offering feedback in a way that mimics human interaction. Khan Academy, for example, utilizes AI to personalize learning paths for millions of students worldwide.
Automation of Administrative Tasks
AI significantly reduces the administrative burden on educators, freeing up valuable time for teaching and student interaction. AI-powered systems can automate tasks such as grading assignments, scheduling classes, and managing student records. This automation streamlines administrative processes, increasing efficiency and reducing errors. For example, AI-powered grading tools can quickly assess multiple-choice tests and provide immediate feedback to students, allowing teachers to focus on more complex assessments and individualized instruction.
By handling repetitive tasks, AI allows educators to dedicate more time to what truly matters: fostering student learning and development.
Enhanced Accessibility for Diverse Learners
AI has the potential to create a more inclusive and equitable learning environment for students with diverse learning needs. AI-powered tools can translate languages in real-time, provide text-to-speech and speech-to-text capabilities, and offer personalized support for students with disabilities. For instance, students with visual impairments can benefit from AI-powered screen readers, while students with auditory processing difficulties can utilize AI-powered captioning and transcription services.
AI can also personalize learning materials to accommodate different learning styles and cognitive abilities, ensuring all students have equal access to quality education. The use of AI-powered assistive technologies is steadily breaking down barriers to education, creating a more equitable and inclusive learning environment for all.
Comparison of Traditional and AI-Assisted Teaching Methods
| Feature | Traditional Teaching Methods | AI-Assisted Teaching Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Lesson Planning | Manual, time-consuming | AI-powered tools suggest lesson plans and resources based on student data and learning objectives. |
| Assessment | Primarily teacher-graded, time-consuming | AI automates grading of objective assessments, provides immediate feedback, and identifies areas needing improvement. |
| Individualized Learning | Limited, often reliant on differentiated instruction | Adaptive learning platforms adjust to individual student needs and pace. |
| Accessibility | Relies on individual accommodations | AI-powered tools provide real-time translation, text-to-speech, and other assistive technologies. |
AI and Communication

Artificial intelligence is profoundly reshaping the landscape of communication, impacting how we translate languages, interact online, receive customer service, and combat misinformation. Its influence spans personal interactions, global collaborations, and the fight for truth in the digital age. This section explores the multifaceted ways AI is altering the fabric of communication.AI’s impact on communication is evident across various platforms and applications, from enhancing cross-cultural understanding to streamlining customer service and battling the spread of false information.
The implications are far-reaching, affecting individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
AI-Powered Language Translation and Cross-Cultural Communication
AI-driven language translation tools are breaking down communication barriers across cultures. Services like Google Translate and DeepL leverage sophisticated neural machine translation (NMT) models to provide increasingly accurate and nuanced translations in real-time. This facilitates international business collaborations, promotes cross-cultural understanding, and enhances access to information for individuals worldwide. For instance, the ability to instantly translate conversations allows for more effective communication in international negotiations, medical emergencies, and tourism.
The increasing accuracy and contextual understanding of NMT are also improving the quality of subtitles and dubbing for films and television shows, making global entertainment more accessible.
AI’s Role in Social Media and Online Interactions
AI algorithms are central to the functioning of social media platforms. They personalize content feeds, recommend connections, and detect potentially harmful content. However, this personalization can also contribute to filter bubbles and echo chambers, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. AI-powered sentiment analysis tools are used to monitor public opinion and brand reputation, while chatbots manage user inquiries and provide automated customer support.
The use of AI in social media presents both opportunities and challenges, raising concerns about privacy, bias, and the spread of misinformation. For example, Facebook utilizes AI to identify and remove hate speech and terrorist content, while Twitter employs AI to detect and flag misleading information.
AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants in Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service by providing 24/7 support, automating routine tasks, and improving response times. Companies use these tools to handle frequently asked questions, resolve simple issues, and guide customers to appropriate resources. This reduces the workload on human customer service representatives, allowing them to focus on more complex and demanding tasks. Examples include banking institutions using chatbots to answer account balance inquiries and e-commerce companies using virtual assistants to help customers navigate their websites and complete purchases.
While these AI systems improve efficiency, concerns remain regarding the limitations of their empathy and ability to handle nuanced or unexpected customer requests.
AI’s Use in Detecting and Combating Misinformation Online
The spread of misinformation and disinformation online poses a significant threat to individuals and society. AI is increasingly being used to detect and combat this issue. Algorithms can analyze text, images, and videos to identify patterns and characteristics consistent with fake news or propaganda. These systems can flag potentially misleading content for human review or automatically remove it from platforms.
However, the development of sophisticated AI-powered misinformation campaigns poses a challenge, highlighting the need for ongoing research and development in this area. For instance, fact-checking organizations are employing AI to help them identify and verify claims made online, while social media companies are using AI to flag potentially false or misleading information in posts and tweets.
AI and Creativity
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the creative landscape, challenging traditional notions of artistry and sparking both excitement and apprehension. Its ability to generate novel outputs in various creative fields raises profound questions about the nature of creativity itself and the role of humans in the creative process. This section explores the multifaceted impact of AI on creativity, examining its applications, ethical implications, and the evolving relationship between human and artificial intelligence in creative endeavors.AI’s capacity to generate art, music, and literature is rapidly advancing.
Algorithms are trained on massive datasets of existing creative works, learning patterns and styles to produce original pieces. This is achieved through various techniques, including generative adversarial networks (GANs), which pit two neural networks against each other to refine outputs, and transformer models, known for their ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
AI-Generated Creative Content: Applications and Examples
AI tools are now capable of producing a wide range of creative content. For instance, AI art generators like DALL-E 2 and Midjourney can create stunning and unique images from text prompts, allowing users to specify details like style, subject matter, and mood. In music, AI systems like Amper Music compose original soundtracks tailored to specific needs, while in literature, AI can generate poems, scripts, and even novels, mimicking various writing styles.
For example, the AI-generated novel “1 the Road” demonstrated the capability of AI to produce lengthy, coherent narratives. These applications are revolutionizing various creative industries, offering new possibilities for artists and designers while also raising ethical concerns.
Ethical Considerations of AI-Generated Creative Content
The rise of AI-generated creative content brings forth several significant ethical considerations. One key issue is copyright and ownership. Determining who owns the copyright to AI-generated works—the programmer, the user who provides the prompt, or the AI itself—is a complex legal question currently without clear answers. Furthermore, concerns about potential biases embedded in training datasets are paramount.
If the data used to train an AI reflects existing societal biases, the AI’s output may perpetuate or even amplify these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. The potential for AI to be used for malicious purposes, such as generating deepfakes or creating propaganda, also poses a serious ethical challenge. Finally, the potential displacement of human artists and creators needs careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
Human Creativity vs. AI-Driven Creativity: A Comparison
While AI can generate impressive creative outputs, it’s crucial to distinguish between human and AI-driven creativity. Human creativity is often characterized by its emotional depth, originality stemming from lived experiences and personal perspectives, and its ability to break established conventions. AI, on the other hand, operates based on patterns and data it has been trained on, lacking the subjective experiences and emotional intelligence that fuel human creativity.
AI can be a powerful tool for enhancing human creativity, but it is not a replacement for the uniquely human aspects of artistic expression. It excels at generating variations on existing themes and styles, but the ability to create truly groundbreaking, paradigm-shifting works still resides firmly within the realm of human ingenuity.
AI as a Tool for Enhancing the Creative Process
Despite the potential for displacement, AI is increasingly being used as a tool to enhance the creative process for artists and designers. AI can automate tedious tasks, such as image editing or music transcription, freeing up artists to focus on the more conceptual and expressive aspects of their work. AI can also provide inspiration and new ideas by suggesting variations on existing works or generating unexpected combinations of styles and elements.
For example, AI tools can assist in the creation of intricate designs or complex musical compositions, acting as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement for human creativity. The future likely involves a symbiotic relationship, where humans and AI work together to push the boundaries of artistic expression.
Challenges and Concerns of AI
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence presents numerous benefits, but it also raises significant ethical, societal, and practical challenges. Understanding these concerns is crucial for ensuring the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies that benefit humanity as a whole. Failure to address these challenges could lead to unforeseen and potentially harmful consequences.
Algorithmic Bias and Societal Impact
AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases (e.g., gender, racial, or socioeconomic), the resulting AI systems will perpetuate and even amplify these biases. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in areas such as loan applications, hiring processes, and even criminal justice. For example, facial recognition systems have been shown to be less accurate in identifying individuals with darker skin tones, potentially leading to misidentification and wrongful accusations.
The societal impact of biased AI is far-reaching, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities and creating new forms of discrimination. Mitigating algorithmic bias requires careful data curation, algorithmic auditing, and ongoing monitoring of AI systems for discriminatory outcomes.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AI systems often rely on the collection and analysis of massive amounts of personal data. This raises significant concerns about data privacy and security. Breaches of this data could lead to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage. Furthermore, the use of AI for surveillance purposes raises concerns about potential abuses of power and erosion of civil liberties.
Robust data protection measures, including encryption, anonymization techniques, and strong access controls, are essential to mitigate these risks. Transparency regarding data collection and usage practices is also crucial to building public trust.
Responsible AI Development and Deployment
Responsible AI development requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes ethical considerations throughout the entire lifecycle of an AI system, from design and development to deployment and monitoring. This includes careful consideration of potential biases, risks, and unintended consequences. Collaboration between AI developers, policymakers, ethicists, and the public is crucial to establish shared principles and guidelines for responsible AI. Furthermore, mechanisms for accountability and redress in cases of AI-related harm need to be established.
Guidelines for Ethical AI Development
A set of ethical guidelines for AI development should prioritize transparency and accountability. These guidelines should emphasize: (1) Explainability: AI systems should be designed to be understandable and interpretable, allowing users to understand how decisions are made. (2) Fairness: AI systems should be designed and deployed in a way that avoids discrimination and promotes fairness. (3) Privacy: AI systems should respect individual privacy and protect sensitive data.
(4) Accountability: Clear lines of responsibility should be established for the development, deployment, and use of AI systems. (5) Human Oversight: Humans should retain ultimate control over AI systems and be able to intervene when necessary. These guidelines should be implemented through a combination of technical measures, regulatory frameworks, and industry self-regulation. Regular audits and independent evaluations of AI systems are essential to ensure compliance with these ethical principles.
Final Thoughts
Artificial intelligence is not merely a technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with the world. While the potential benefits—increased efficiency, personalized experiences, and innovative solutions to complex problems—are vast, responsible development and deployment are paramount. Addressing ethical concerns, mitigating biases, and ensuring data privacy are crucial steps in harnessing AI’s power for the betterment of humanity.
The future shaped by AI will be a reflection of the choices we make today.

