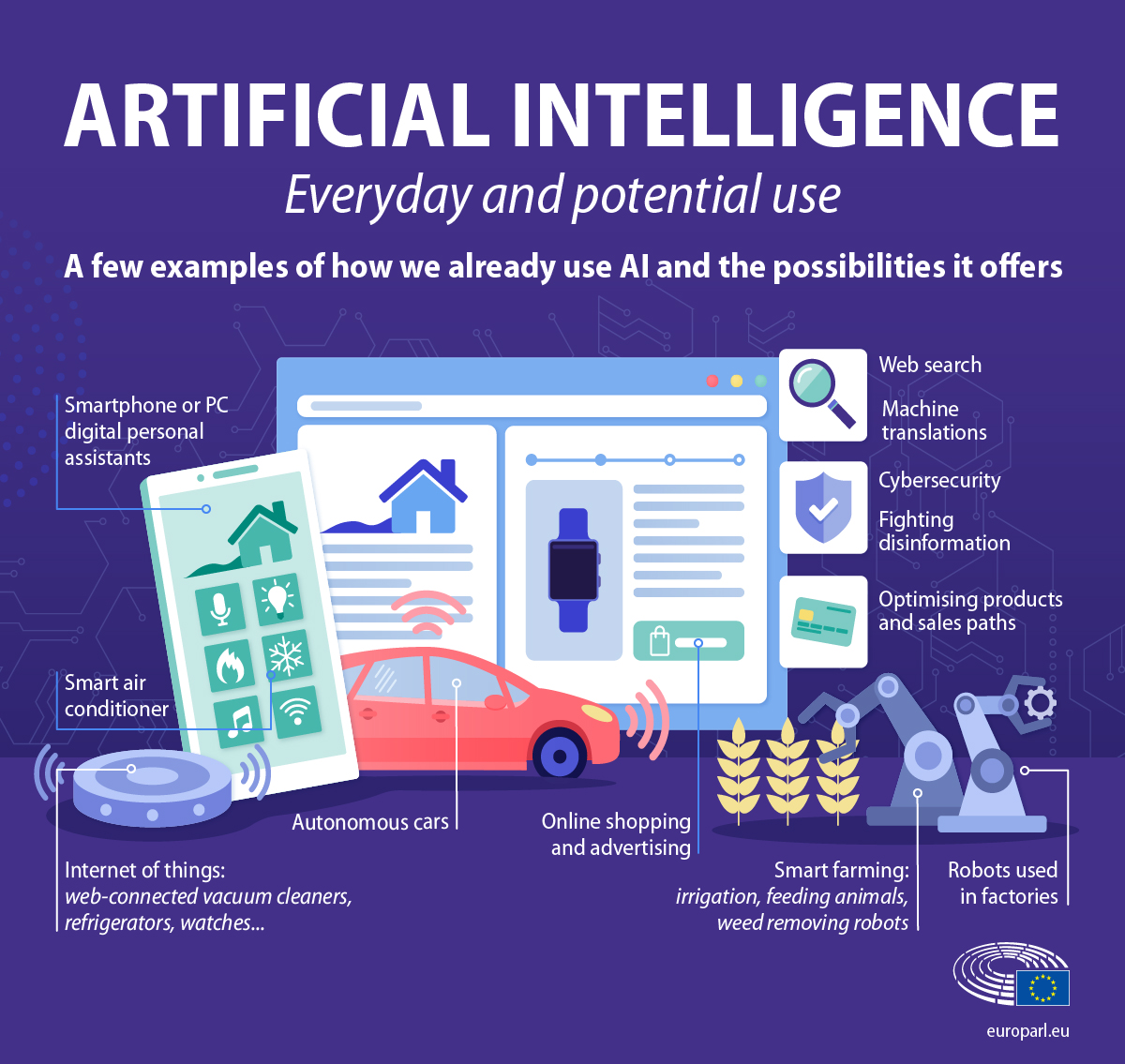
What are the everyday applications of artificial intelligence? The answer is increasingly ubiquitous, weaving its way into the fabric of modern life. From the seemingly simple convenience of predictive text on our smartphones to the complex algorithms powering self-driving cars, AI is quietly revolutionizing how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. This exploration delves into the diverse ways AI impacts our daily routines, revealing its pervasive influence and future potential.
We’ll examine AI’s role in various sectors, from enhancing our mobile experiences and transforming transportation to revolutionizing healthcare and reshaping the retail landscape. We will also explore its impact on social media and entertainment, highlighting both its benefits and potential challenges. By understanding these applications, we can better appreciate the transformative power of AI and its ongoing evolution.
Smartphones and AI: What Are The Everyday Applications Of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become deeply integrated into the fabric of modern smartphones, enhancing user experience and functionality in numerous ways. From the seemingly simple act of typing a text message to the complex task of navigating using voice commands, AI algorithms are constantly at work, making our interactions with these devices smoother and more efficient. This integration, however, also raises important considerations regarding data privacy and security.
AI-Powered Smartphone Features
AI powers a wide range of features within smartphones. Voice assistants, such as Siri and Google Assistant, utilize natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to understand and respond to user voice commands. These assistants can perform tasks ranging from setting reminders and making calls to providing information and controlling smart home devices. Predictive text, another common feature, leverages AI to anticipate the user’s next word or phrase, significantly speeding up typing.
Image recognition capabilities, found in many camera apps, employ deep learning algorithms to identify objects, scenes, and faces within photographs, often providing contextual information or suggesting filters and edits.
Personalized Recommendations in Smartphones
The algorithms behind personalized recommendations in apps and operating systems rely on machine learning techniques, specifically recommendation systems. These systems analyze user data, such as app usage, browsing history, location data, and purchase patterns, to predict preferences and suggest relevant content, apps, or products. Collaborative filtering, a common technique, identifies users with similar preferences and recommends items that those users have enjoyed.
Content-based filtering, on the other hand, focuses on the characteristics of the items themselves to suggest similar ones. For example, if a user frequently listens to a particular genre of music, a content-based filtering system would recommend similar artists or albums. These systems are constantly learning and adapting, refining their recommendations based on user interactions.
Security Implications of AI in Smartphones
The increasing reliance on AI in smartphones presents significant security challenges. AI-powered features often require access to vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy violations and potential misuse. For example, voice assistants may record conversations, and image recognition algorithms may analyze personal photos. Furthermore, the sophisticated algorithms themselves can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate input data to cause the AI system to behave unexpectedly or produce incorrect results.
This could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or even physical harm in the case of autonomous driving features (although not directly related to the smartphone itself, it highlights the broader security risks). Robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security updates, are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Comparison of AI Capabilities Across Smartphone Operating Systems
The following table compares the AI capabilities of three popular smartphone operating systems: iOS, Android, and HarmonyOS. The comparison is based on the general capabilities offered and may vary slightly depending on the specific device and software version.
| Operating System | Voice Assistant | Image Recognition | Personalized Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | Siri (proficient in natural language understanding, integration with Apple ecosystem) | Robust image recognition within Photos app (object identification, scene detection, facial recognition) | Highly personalized recommendations across Apple services (App Store, Music, News, etc.) |
| Android | Google Assistant (wide range of functionalities, integration with Google services) | Varying capabilities depending on device and manufacturer (generally good object and scene detection) | Personalized recommendations across Google services and many third-party apps |
| HarmonyOS | Celia (improving natural language processing, focused on seamless integration within the HarmonyOS ecosystem) | Image recognition features are integrated into the system and various apps (capabilities are developing) | Personalized recommendations within the HarmonyOS ecosystem and select third-party apps (still under development) |
AI in Transportation
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the transportation sector, impacting everything from individual vehicles to the management of entire transportation networks. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and make complex decisions in real-time is revolutionizing safety, efficiency, and sustainability within the industry. This section will explore the various ways AI is being implemented in transportation systems.
Self-Driving Cars: Object Detection and Navigation
Self-driving cars rely heavily on AI for their functionality. Object detection systems, powered by deep learning algorithms, analyze data from cameras, lidar, and radar to identify and classify objects such as pedestrians, vehicles, and traffic signs. This information is crucial for safe navigation. Simultaneously, sophisticated navigation systems, utilizing AI-powered route planning and path optimization, guide the vehicle to its destination, considering real-time traffic conditions and potential obstacles.
These systems constantly process sensory data, predict the movement of other objects, and make decisions about speed, steering, and braking to ensure a smooth and safe journey. For example, Tesla’s Autopilot system utilizes a combination of cameras and radar to detect obstacles and assist with lane keeping and adaptive cruise control. Waymo’s self-driving technology employs a more comprehensive sensor suite, including lidar, for even greater accuracy in object detection and mapping.
AI-Powered Traffic Flow Optimization
AI is proving invaluable in managing and optimizing traffic flow in urban areas. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) leverage AI algorithms to analyze real-time traffic data from various sources, including traffic cameras, GPS devices, and sensors embedded in roadways. This data is used to identify congestion hotspots, predict traffic patterns, and dynamically adjust traffic signals to improve overall flow.
For instance, some cities are using AI-powered systems to optimize traffic light timing based on real-time traffic conditions, leading to reduced congestion and travel times. Furthermore, AI can assist in predicting potential accidents or incidents based on historical data and current traffic patterns, allowing for proactive interventions to minimize disruption.
AI-Powered Features in Existing Vehicles
Many modern vehicles already incorporate AI-powered features designed to enhance safety and driver assistance. Adaptive cruise control uses AI to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead, automatically adjusting speed to avoid collisions. Lane keeping assist systems utilize AI to detect lane markings and gently steer the vehicle back into its lane if it begins to drift.
Automatic emergency braking (AEB) systems employ AI to detect potential collisions and automatically apply the brakes if necessary. These features, while not fully autonomous, represent significant steps towards increased safety and driver convenience. Examples of vehicles with these features include most modern models from manufacturers such as Toyota, Honda, and Ford.
Decision-Making Process of a Self-Driving Car Encountering an Unexpected Obstacle
A flowchart illustrating the decision-making process of a self-driving car encountering an unexpected obstacle would begin with the sensors (cameras, lidar, radar) detecting the obstacle. This information would be processed by the perception system, which classifies the obstacle (pedestrian, vehicle, debris, etc.) and estimates its trajectory. The planning system then evaluates various options, such as braking, swerving, or slowing down.
The control system executes the chosen action, sending signals to the vehicle’s actuators (steering, brakes, accelerator). Finally, the monitoring system assesses the outcome and makes adjustments if necessary. This process is iterative and constantly refined based on the ever-changing environment. The system must also consider safety constraints and legal regulations in its decision-making.
AI in Healthcare
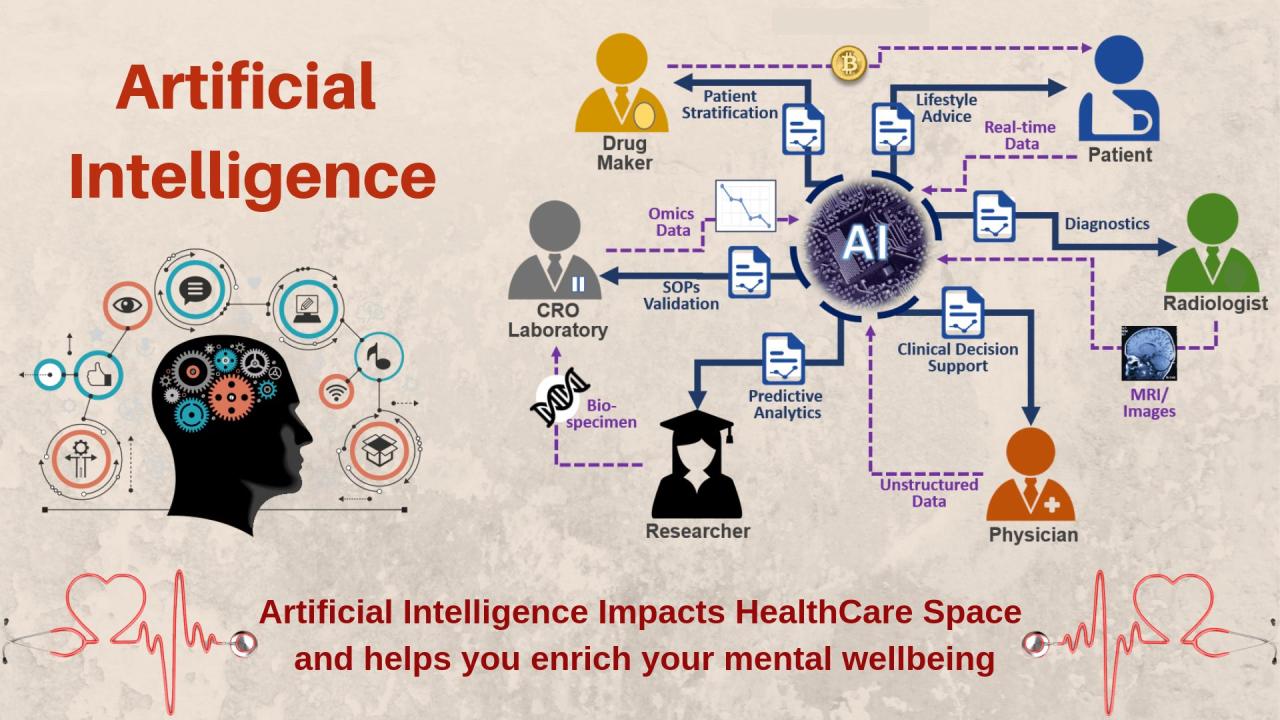
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the healthcare industry, offering innovative solutions to improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. From analyzing medical images to accelerating drug discovery, AI’s impact is profound and far-reaching, promising a future of more personalized and effective healthcare.AI’s role in healthcare is multifaceted, encompassing various applications that aim to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of medical services.
This section explores several key areas where AI is making a significant contribution.
AI in Medical Diagnosis
AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, are proving highly effective in analyzing medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These algorithms can be trained on vast datasets of medical images to identify patterns indicative of diseases like cancer, helping radiologists and other medical professionals make more accurate and timely diagnoses. For example, AI systems can detect subtle anomalies in mammograms that might be missed by the human eye, leading to earlier detection of breast cancer and improved patient outcomes.
Similarly, AI can assist in the diagnosis of other cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders by analyzing relevant imaging data. The speed and accuracy offered by AI-powered diagnostic tools can significantly reduce diagnostic errors and improve the efficiency of healthcare workflows.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
The process of drug discovery and development is traditionally long, expensive, and complex. AI is accelerating this process by analyzing vast amounts of biological data to identify potential drug candidates, predict their efficacy, and optimize their design. Machine learning algorithms can analyze genomic data, protein structures, and clinical trial results to identify promising drug targets and predict the likelihood of success for new drugs.
This significantly reduces the time and cost associated with bringing new therapies to market, potentially leading to faster development of treatments for various diseases. For example, AI has been used to identify new potential drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders by analyzing large datasets of genomic and proteomic information.
AI in Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine aims to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. AI plays a crucial role in achieving this goal by analyzing patient data to predict individual responses to different treatments. By integrating data from electronic health records, genomics, and wearable sensors, AI algorithms can create personalized treatment plans that maximize efficacy and minimize side effects.
For instance, AI can help predict which patients are most likely to respond to a specific cancer therapy, allowing doctors to make more informed treatment decisions. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also optimizes resource allocation in healthcare systems.
Ethical Concerns Related to AI in Healthcare
The use of AI in healthcare presents several ethical considerations that require careful attention. These include:
- Data Privacy and Security: AI systems rely on vast amounts of sensitive patient data, raising concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access. Robust security measures are crucial to protect patient privacy.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing biases, the algorithms may perpetuate or even amplify those biases in healthcare decisions, leading to disparities in care.
- Transparency and Explainability: Understanding how AI algorithms arrive at their decisions is crucial for building trust and accountability. The “black box” nature of some AI models can make it difficult to interpret their outputs and identify potential errors.
- Responsibility and Liability: Determining liability in cases of AI-related medical errors is a complex legal and ethical challenge. Clear guidelines and frameworks are needed to address this issue.
- Access and Equity: The high cost of developing and implementing AI-powered healthcare tools could exacerbate existing health disparities, limiting access for underserved populations.
AI in Retail and E-commerce

Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the retail and e-commerce landscape, impacting everything from how products are recommended to how customer service is delivered and supply chains are managed. The integration of AI offers businesses significant opportunities to enhance efficiency, personalize customer experiences, and ultimately, boost profitability.
AI-Powered Recommendation Engines
Recommendation engines, a cornerstone of modern e-commerce, leverage AI algorithms to analyze vast amounts of customer data, including browsing history, purchase history, and even social media activity. These algorithms identify patterns and predict which products a customer is most likely to be interested in. For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine, known for its “Customers who bought this item also bought…” feature, utilizes collaborative filtering and content-based filtering techniques to suggest relevant products.
This increases sales by exposing customers to items they might not have otherwise discovered, improving customer satisfaction and driving revenue. More sophisticated systems incorporate deep learning models to understand nuanced customer preferences and provide even more personalized recommendations.
AI-Driven Chatbots for Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots are revolutionizing customer service in both online and brick-and-mortar retail settings. These virtual assistants can handle a wide range of customer inquiries, from answering frequently asked questions about product specifications and shipping times to processing returns and providing order updates. For instance, Sephora uses chatbots to provide personalized beauty advice and product recommendations, creating a more engaging and helpful customer experience.
The use of chatbots frees up human customer service representatives to handle more complex issues, leading to increased efficiency and reduced wait times for customers. Moreover, AI-powered chatbots can operate 24/7, providing continuous support to customers regardless of time zone.
AI in Supply Chain Optimization and Inventory Management
AI significantly enhances supply chain management and inventory control by predicting demand, optimizing logistics, and minimizing waste. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors like weather patterns to forecast future demand with greater accuracy. This enables retailers to optimize inventory levels, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Furthermore, AI can optimize delivery routes and warehouse operations, improving efficiency and reducing transportation costs.
For example, Walmart uses AI to predict demand for specific products in different locations, allowing them to efficiently manage their vast supply chain and ensure products are available where and when they are needed.
AI in Brick-and-Mortar Stores vs. Online Retailers, What are the everyday applications of artificial intelligence?
The application of AI differs somewhat between brick-and-mortar and online retailers, although there is considerable overlap.
Here’s a comparison:
- Brick-and-Mortar Stores:
- AI-powered smart shelves track inventory levels in real-time, automatically alerting staff to low stock.
- Computer vision systems analyze customer behavior to optimize store layouts and product placement.
- Robotic process automation handles repetitive tasks like price adjustments and inventory management.
- Online Retailers:
- AI-powered recommendation engines personalize product suggestions based on individual customer preferences.
- AI-driven chatbots provide 24/7 customer support and handle a wide range of inquiries.
- Predictive analytics optimize pricing strategies and marketing campaigns.
AI in Social Media and Entertainment
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the landscape of social media and entertainment, impacting how we consume content, interact with platforms, and even create art. AI algorithms are not merely background processes; they are the driving force behind personalized experiences and the detection of harmful content, fundamentally shaping our digital interactions.AI algorithms personalize content feeds on social media platforms by analyzing vast amounts of user data, including past interactions, likes, shares, and comments.
This data is used to create a profile of each user’s interests and preferences. The algorithms then use this profile to select and prioritize content that is most likely to engage the user, resulting in a highly personalized feed. This personalization, while effective in keeping users engaged, also raises concerns about filter bubbles and echo chambers, potentially limiting exposure to diverse perspectives.
AI-Driven Content Personalization on Social Media
Social media platforms utilize sophisticated machine learning models to predict user preferences. These models consider various factors such as post engagement (likes, comments, shares), browsing history, search queries, and even the time of day a user is most active. By analyzing this data, the algorithms identify patterns and correlations to tailor the content feed accordingly. For instance, if a user consistently interacts with posts about sustainable living, the algorithm will prioritize similar content in their feed, potentially leading to a more focused and engaging experience.
However, this approach can also result in users being presented with a limited range of viewpoints, reinforcing existing beliefs and potentially isolating them from alternative perspectives.
AI in Content Moderation and Fake News Detection
AI plays a crucial role in content moderation, helping platforms manage the massive volume of user-generated content. AI algorithms are trained to identify and flag potentially harmful content, such as hate speech, violence, and misinformation. These algorithms utilize natural language processing (NLP) to analyze text, images, and videos, identifying patterns and s associated with inappropriate content. Similarly, AI is employed to detect and flag fake news articles and deepfakes.
These systems analyze the source of information, cross-reference claims with established facts, and identify inconsistencies in the narrative to flag potentially misleading content. Despite their effectiveness, these AI systems are not perfect and can sometimes misidentify legitimate content or fail to detect sophisticated forms of misinformation.
Examples of AI-Generated Art, Music, and Literature
AI is increasingly used to create art, music, and literature. Several AI tools can generate unique images from textual descriptions, allowing users to create personalized artwork without artistic skills. AI-powered music composition tools can generate melodies, harmonies, and rhythms, offering new possibilities for musicians and composers. Similarly, AI can be used to generate different writing styles and creative text formats.
For example, OpenAI’s GPT-3 can generate human-quality text, including poems, scripts, and articles, pushing the boundaries of creative writing. These AI tools demonstrate the potential of AI to democratize creative processes and offer new avenues for artistic expression.
A Hypothetical Future Scenario: AI in Entertainment
Imagine a future where AI curates personalized entertainment experiences with unprecedented accuracy. A user puts on a virtual reality headset and is instantly transported to a unique, AI-generated world tailored to their preferences. The story unfolds dynamically, adapting to their choices and reactions in real-time. AI-driven characters evolve and interact naturally, creating a truly immersive and interactive experience.
This future isn’t just about passive consumption; it’s about active participation in a constantly evolving, AI-powered narrative landscape. The entertainment industry would shift from producing pre-packaged content to creating dynamic, personalized worlds tailored to each individual’s preferences, opening up limitless possibilities for creative storytelling and audience engagement.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the everyday applications of artificial intelligence are far-reaching and profoundly impactful. From the seemingly mundane tasks of personalized recommendations to the groundbreaking advancements in healthcare and autonomous vehicles, AI is reshaping our world in ways we are only beginning to understand. As AI technology continues to advance, its integration into our daily lives will only become more seamless and transformative, presenting both incredible opportunities and important ethical considerations that require careful consideration.

