Big data and AI: a new era of business competitiveness. This isn’t just hype; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, compete, and thrive. The ability to harness the power of massive datasets and sophisticated algorithms is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for survival in today’s rapidly evolving marketplace. This exploration delves into the transformative impact of big data and AI, examining its applications across various industries, the competitive advantages it offers, and the challenges businesses must overcome to fully leverage its potential.
We’ll dissect the core concepts of big data and AI, comparing them to traditional business analytics and exploring different AI learning models used for data analysis. From predictive analytics forecasting market trends to optimizing supply chains and enhancing customer experiences, we’ll examine real-world applications and case studies showcasing the tangible benefits. Crucially, we’ll also address the ethical considerations, potential biases, and security risks inherent in these powerful technologies, providing a balanced and comprehensive overview of this transformative era.
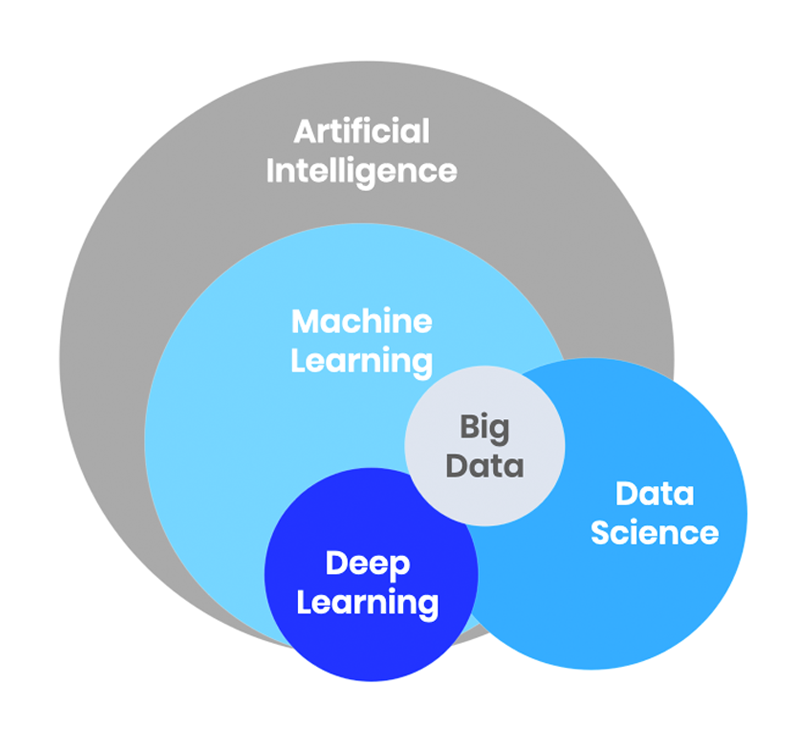
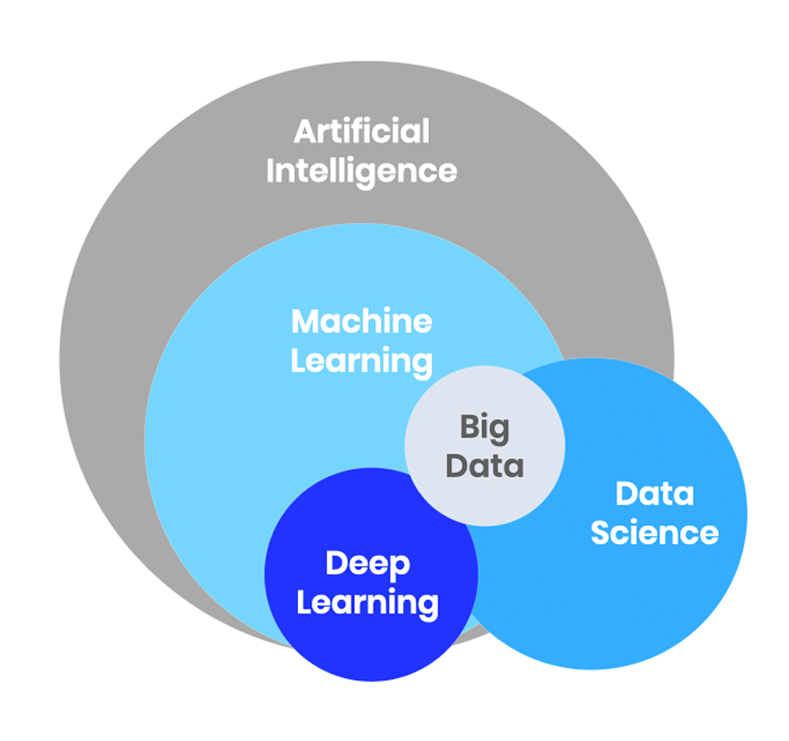
Defining Big Data and AI in Business Context
Big data and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the business landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for enhanced efficiency, improved decision-making, and competitive advantage. Understanding the characteristics of big data and the diverse applications of AI is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage these technologies effectively.
Big Data Characteristics in a Business Context
Big data, in a business context, refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are difficult to process using traditional data processing applications. These datasets possess several key characteristics, often summarized as the “five Vs”: Volume (the sheer size of the data), Velocity (the speed at which data is generated and processed), Variety (the diverse formats of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data), Veracity (the accuracy and reliability of the data), and Value (the potential insights and business benefits that can be derived from the data).
These characteristics present both challenges and opportunities for businesses. For example, the high volume of transactional data generated by e-commerce platforms provides valuable insights into customer behavior, but requires sophisticated tools and techniques for effective analysis. Similarly, the velocity of social media data necessitates real-time processing capabilities to capture emerging trends and sentiment.
AI Algorithm Applications in Big Data Analysis Across Industries
AI algorithms are instrumental in analyzing big data to extract meaningful insights and drive business decisions. Various industries leverage different AI techniques depending on their specific needs. For example, in the financial services industry, machine learning algorithms are used for fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. These algorithms analyze vast transactional data to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities or predict market trends.
In healthcare, AI algorithms analyze medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) to aid in diagnosis, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. Retail uses AI-powered recommendation systems, analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior to suggest relevant products, increasing sales and customer satisfaction. Manufacturing employs AI for predictive maintenance, analyzing sensor data from machinery to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Traditional Business Analytics vs. Big Data and AI Capabilities
Traditional business analytics often relies on smaller, structured datasets and simpler statistical methods. While effective for analyzing historical data, it struggles with the volume, velocity, and variety of big data. Big data and AI, on the other hand, offer significantly enhanced capabilities. They can handle massive datasets, process data in real-time, and analyze diverse data types including text, images, and sensor data.
Furthermore, AI algorithms can identify complex patterns and relationships that are invisible to traditional methods, enabling more accurate predictions and improved decision-making. The ability to perform predictive analytics, generate personalized recommendations, and automate tasks are key differentiators that provide a significant competitive advantage. For instance, a traditional business might analyze past sales figures to predict future demand, whereas a big data and AI-driven approach could incorporate real-time social media sentiment, economic indicators, and weather data for a much more nuanced and accurate forecast.
Types of AI Used in Big Data Analysis
| AI Type | Description | Example in Big Data Analysis | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Algorithms learn from labeled data to predict outcomes. | Predicting customer churn based on historical customer data with known churn outcomes. | High accuracy in prediction tasks with labeled data. |
| Unsupervised Learning | Algorithms identify patterns and structures in unlabeled data. | Customer segmentation based on purchase history and demographics without pre-defined segments. | Discovers hidden patterns and relationships in data. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Algorithms learn through trial and error by interacting with an environment. | Optimizing pricing strategies by learning from the impact of different price points on sales. | Adapts and improves over time through interaction. |
| Deep Learning | A subfield of machine learning using artificial neural networks with multiple layers. | Image recognition for analyzing product images in e-commerce to improve search and categorization. | Handles complex patterns and large datasets effectively. |
Competitive Advantages Through Big Data and AI
The convergence of big data and artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing business operations, creating unprecedented opportunities for competitive advantage. Companies leveraging these technologies effectively are able to make faster, more informed decisions, anticipate market shifts, and personalize customer experiences in ways previously unimaginable. This leads to improved efficiency, increased revenue, and stronger market positioning. The ability to extract meaningful insights from massive datasets allows for a level of strategic precision that was once the domain of speculation and guesswork.Real-time data analysis powered by AI significantly enhances decision-making speed and accuracy.
Traditional methods of business intelligence often rely on lagging indicators and historical data, providing a rearview mirror perspective. In contrast, AI algorithms can process streaming data in real-time, identifying trends and anomalies as they emerge. This allows businesses to respond proactively to market changes, optimize operations dynamically, and personalize customer interactions instantaneously. For instance, a retailer can instantly adjust pricing based on real-time demand fluctuations or a financial institution can detect and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time.
Real-time Data Analysis and Decision-Making
Real-time data analysis, facilitated by AI, empowers businesses to make rapid and accurate decisions. AI algorithms can process vast quantities of data from diverse sources—including sales figures, social media sentiment, website traffic, and sensor data—to identify patterns and trends that would be impossible for humans to detect manually. This speed and accuracy translates directly into improved operational efficiency, better resource allocation, and more effective risk management.
Consider a logistics company utilizing AI to optimize delivery routes based on real-time traffic conditions. By adapting routes dynamically, the company can reduce delivery times, minimize fuel consumption, and improve customer satisfaction. The speed and precision offered by real-time analysis provide a significant competitive edge in today’s dynamic market.
Predictive Analytics and Market Trend Forecasting
Predictive analytics, a key application of AI, enables businesses to forecast market trends and anticipate customer behavior with greater accuracy. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, AI algorithms can predict future outcomes with a higher degree of confidence than traditional forecasting methods. This allows businesses to proactively adjust their strategies, optimize resource allocation, and gain a first-mover advantage in emerging markets.
For example, a consumer goods company can use predictive analytics to anticipate changes in consumer preferences and adjust its product development accordingly. A financial institution might use predictive analytics to identify potential risks and opportunities in the market, enabling it to make more informed investment decisions.
Competitive Advantages Across Business Functions
Big data and AI offer significant competitive advantages across various business functions. In marketing, AI-powered personalization engines deliver targeted advertising campaigns and customized customer experiences, leading to improved conversion rates. In sales, AI-driven CRM systems predict customer churn, identify high-value leads, and automate sales processes, resulting in increased revenue and reduced costs. In operations, AI optimizes supply chain management, predicts equipment failures, and automates repetitive tasks, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Hypothetical Scenario: AI-Powered Competitive Advantage
Imagine a retail clothing company, “StyleWise,” that uses AI to analyze vast amounts of customer data, including purchase history, browsing behavior, social media interactions, and even weather patterns. StyleWise’s AI system identifies emerging fashion trends weeks before they become mainstream. This allows StyleWise to adjust its inventory, optimize its marketing campaigns, and even design new products tailored to these anticipated trends.
Competitors relying on traditional market research methods are slower to react, resulting in StyleWise gaining a significant market share and higher profitability. The company’s AI system also personalizes customer experiences by recommending relevant products and offering targeted discounts, leading to increased customer loyalty and repeat business. This scenario demonstrates how AI-powered big data insights can create a powerful competitive advantage, enabling a company to outperform its rivals in speed, agility, and customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Risks of Big Data and AI Implementation
The transformative potential of big data and AI is undeniable, yet their implementation presents significant challenges and risks that businesses must carefully consider. Failure to address these issues can lead to project failure, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. This section delves into the key hurdles businesses face when integrating these technologies.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns in Big Data Applications
The sheer volume and sensitivity of data involved in big data applications significantly increase the risk of breaches and privacy violations. Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive customer information, intellectual property, and other valuable assets. This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption protocols, and regular security audits. Failure to adequately protect data can result in hefty fines under regulations like GDPR and CCPA, alongside irreparable damage to brand reputation and customer trust.
For example, a healthcare provider failing to properly secure patient data could face millions of dollars in fines and a loss of public confidence. Furthermore, sophisticated cyberattacks targeting vulnerabilities in data storage and processing pipelines pose a constant threat, necessitating proactive security strategies.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Big Data and AI Solutions Across Business Sizes
The cost of implementing big data and AI solutions varies considerably depending on the scale of the business and the complexity of the project. Small businesses might find the initial investment prohibitive, requiring careful consideration of return on investment (ROI). Larger enterprises, on the other hand, often have the resources to invest in more sophisticated technologies and skilled personnel, potentially achieving greater returns.
However, even large corporations can face challenges in managing the ongoing costs of data storage, maintenance, and talent acquisition. A small startup might benefit from cloud-based solutions offering scalable resources, while a large multinational corporation might opt for on-premise solutions to maintain tighter control over its data. The key is to carefully assess the specific needs and capabilities of the business before committing to a particular solution.
For instance, a small e-commerce business might prioritize a cost-effective analytics platform for customer behavior analysis, while a large financial institution might invest heavily in fraud detection AI.
Ethical Concerns Related to AI-Driven Decision-Making
The increasing reliance on AI in business decision-making raises several ethical concerns. Algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, and potential for discrimination are major issues. AI systems trained on biased data can perpetuate and amplify existing societal inequalities, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For example, an AI system used for loan applications trained on historical data reflecting discriminatory lending practices might unfairly deny loans to certain demographic groups.
The lack of transparency in how some AI algorithms make decisions makes it difficult to identify and rectify such biases, raising concerns about accountability and fairness. Businesses need to implement robust ethical frameworks to guide the development and deployment of AI systems, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability. This includes rigorous testing for bias, regular audits of AI systems, and mechanisms for human oversight.
Potential Biases in AI Algorithms and Their Impact on Business Outcomes
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing biases, the algorithm will likely perpetuate those biases. This can lead to inaccurate predictions, unfair decisions, and ultimately, negative business outcomes. For example, a facial recognition system trained primarily on images of individuals from one racial group might perform poorly when identifying individuals from other groups.
In a hiring process, this could lead to discriminatory outcomes. Similarly, a marketing algorithm trained on biased data might target certain demographic groups unfairly. Addressing bias requires careful data curation, algorithmic auditing, and the development of more robust and equitable AI models. Businesses must actively work to mitigate bias in their AI systems to ensure fairness, avoid legal challenges, and maintain their reputation.
Future Trends and Implications

The convergence of big data and AI is not a static phenomenon; it’s a rapidly evolving landscape shaped by continuous technological advancements and shifting business needs. Understanding the future trends and their implications is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge in this data-driven world. This section explores emerging technologies, the evolving roles of data professionals, the impact on the job market, and a projected timeline for the next decade of big data and AI applications in business.
The integration of big data and AI is poised for significant acceleration, driven by breakthroughs in several key areas. This will fundamentally alter how businesses operate, compete, and interact with their customers.
Emerging Technologies Integrating Big Data and AI
The next generation of big data and AI applications will be significantly influenced by advancements in several key areas. These technologies will not only enhance existing capabilities but also unlock entirely new possibilities for businesses.
Several emerging technologies are poised to further integrate big data and AI in business. These include advancements in:
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers, with their potential to process vast datasets exponentially faster than classical computers, will revolutionize AI algorithms, enabling the development of more sophisticated and accurate predictive models. Imagine a scenario where drug discovery, financial modeling, or supply chain optimization are accelerated by orders of magnitude, leading to significant breakthroughs and cost savings.
- Edge AI: Processing data closer to its source (the “edge”) reduces latency and bandwidth requirements, making real-time AI applications more feasible in areas like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart cities. This means faster responses, reduced reliance on cloud infrastructure, and improved efficiency in data-intensive processes.
- Generative AI: Models like large language models (LLMs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) are enabling businesses to automate content creation, personalize customer experiences, and design innovative products and services. This translates to increased productivity, improved marketing effectiveness, and the ability to offer highly customized solutions.
- Explainable AI (XAI): The increasing demand for transparency and accountability in AI systems is driving the development of XAI techniques, which aim to make AI decision-making more understandable and interpretable. This fosters trust and allows businesses to better understand and manage the risks associated with AI deployment.
Evolving Roles of Data Scientists and AI Specialists
The roles of data scientists and AI specialists are evolving rapidly, demanding a broader skillset and deeper understanding of business contexts.
The increasing sophistication of big data and AI necessitates a shift in the skillset and responsibilities of data scientists and AI specialists. These professionals are no longer solely focused on technical aspects but are increasingly required to collaborate closely with business stakeholders to solve real-world problems.
- Increased Collaboration: Data scientists are increasingly working alongside business leaders, domain experts, and other stakeholders to ensure AI solutions align with business objectives and ethical considerations.
- Focus on Business Outcomes: The emphasis is shifting from simply building models to delivering tangible business value. This requires a strong understanding of business processes, metrics, and strategic goals.
- Expertise in Multiple Domains: Data scientists and AI specialists are increasingly expected to possess expertise in multiple areas, including data engineering, machine learning, cloud computing, and data visualization.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of AI are becoming increasingly important, requiring data professionals to understand and address biases, fairness, and privacy concerns.
Impact of Big Data and AI on Job Markets and Workforce Skills
The widespread adoption of big data and AI is transforming the job market, creating new opportunities while rendering some existing roles obsolete.
The impact of big data and AI on the job market is multifaceted, presenting both challenges and opportunities. Adaptability and continuous learning will be crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
- Job Displacement in Certain Sectors: Automation driven by AI is likely to displace workers in certain sectors, particularly those involving repetitive or manual tasks. However, this displacement will likely be offset by the creation of new roles requiring specialized skills.
- Creation of New Roles: The demand for professionals with expertise in data science, AI, and related fields is expected to continue growing rapidly. This includes roles such as AI ethicists, data engineers, and AI trainers.
- Need for Upskilling and Reskilling: Workers in many industries will need to acquire new skills to remain competitive in the evolving job market. This includes developing proficiency in data analysis, AI literacy, and digital technologies.
- Emphasis on Human-AI Collaboration: The future of work is likely to involve greater collaboration between humans and AI, requiring workers to develop skills in working effectively with AI systems.
Timeline for the Evolution of Big Data and AI Applications in Business (Next Decade), Big data and AI: a new era of business competitiveness
Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but based on current trends, a plausible timeline for the evolution of big data and AI applications in business over the next decade can be constructed.
The following timeline provides a potential trajectory for the evolution of big data and AI applications in business over the next decade. It’s important to note that this is a projection, and the actual pace of development may vary.
| Year | Anticipated Development | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-2026 | Widespread adoption of generative AI for marketing, customer service, and content creation. Increased use of edge AI in manufacturing and logistics. | Personalized marketing campaigns driven by generative AI, automated customer support chatbots, real-time inventory optimization in warehouses using edge AI. |
| 2027-2029 | Maturation of explainable AI (XAI) leading to greater trust and adoption of AI systems in high-stakes decisions. Increased use of quantum computing for specific applications. | AI-powered financial risk assessment with transparent explanations, drug discovery accelerated by quantum computing simulations. |
| 2030-2034 | Integration of AI across all aspects of business operations, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity. Development of more sophisticated AI models capable of handling complex, unstructured data. | Fully automated supply chains, AI-driven personalized healthcare, predictive maintenance in infrastructure management. |
Case Studies: Big Data And AI: A New Era Of Business Competitiveness
Successful implementations of big data and AI across various industries demonstrate the transformative potential of these technologies. The following case studies highlight how organizations have leveraged these tools to achieve significant improvements in customer experience, supply chain management, and operational efficiency. Each example provides valuable insights into the strategies, challenges, and ultimate benefits realized.
Netflix: Enhanced Customer Experience Through Big Data and AI
Netflix utilizes big data and AI extensively to personalize its content recommendations and improve user experience. Through sophisticated algorithms analyzing viewing history, ratings, and search patterns, Netflix predicts user preferences with remarkable accuracy. This personalized approach leads to increased user engagement, longer viewing times, and reduced churn. The company’s recommendation engine, a core component of its success, continuously learns and adapts, refining its predictions based on real-time user interactions.
This data-driven approach allows Netflix to offer highly relevant content, enhancing user satisfaction and fostering customer loyalty. The success of Netflix’s approach underscores the power of big data and AI in creating deeply personalized and engaging digital experiences.
Walmart: Optimizing Supply Chain Management with AI-Powered Forecasting
Walmart, a global retail giant, leverages big data and AI to optimize its complex supply chain. The company uses machine learning models to predict demand fluctuations, enabling more accurate inventory management. By analyzing historical sales data, weather patterns, social media trends, and even local events, Walmart can anticipate changes in consumer behavior and adjust its inventory levels accordingly.
This precise forecasting minimizes stockouts and overstocking, reducing waste and optimizing logistics. The result is a more efficient and cost-effective supply chain, enabling Walmart to maintain competitive pricing and enhance its overall operational efficiency. This example showcases the significant impact of AI-driven forecasting on supply chain optimization.
General Electric (GE): Improving Operational Efficiency and Reducing Costs Through Predictive Maintenance
GE utilizes big data and AI to implement predictive maintenance across its industrial equipment. By collecting sensor data from its turbines, engines, and other machinery, GE can identify potential equipment failures before they occur. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to predict maintenance needs, allowing GE to schedule maintenance proactively rather than reactively. This prevents costly downtime, reduces repair expenses, and extends the lifespan of equipment.
This data-driven approach to maintenance demonstrates the significant cost savings and efficiency gains achievable through AI-powered predictive analytics in industrial settings. The proactive nature of the system ensures minimal disruption and maximizes asset utilization.
| Company | Application | Key Outcomes | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | Personalized Content Recommendations | Increased user engagement, longer viewing times, reduced churn | Accurate data collection and algorithm refinement are crucial for success. |
| Walmart | AI-Powered Supply Chain Forecasting | Minimized stockouts and overstocking, reduced waste, optimized logistics | Real-time data integration and continuous model improvement are essential. |
| General Electric (GE) | Predictive Maintenance | Reduced downtime, lower repair costs, extended equipment lifespan | High-quality sensor data and robust machine learning models are necessary. |
Wrap-Up
The convergence of big data and AI is reshaping the competitive landscape, creating unprecedented opportunities for businesses willing to embrace the change. While challenges related to data security, ethical considerations, and implementation costs exist, the potential rewards—improved decision-making, enhanced efficiency, and innovative new business models—far outweigh the risks. Companies that proactively invest in robust data infrastructure, skilled talent, and ethical AI frameworks will be best positioned to harness the full potential of this transformative technology and secure a leading edge in the years to come.
The future of business is data-driven, and those who adapt will thrive.