Big data and AI integration for improved business efficiency is revolutionizing how businesses operate. By harnessing the power of massive datasets and sophisticated algorithms, companies can unlock unprecedented levels of insight, automate complex processes, and ultimately, achieve significant gains in efficiency. This exploration delves into the strategies, architectures, and real-world applications that are driving this transformation, examining both the opportunities and challenges involved.
From optimizing supply chains and enhancing customer service to improving predictive analytics and streamlining decision-making, the integration of big data and AI offers a powerful toolkit for businesses of all sizes. We’ll explore the various approaches to integration, the role of cloud computing, and the critical importance of data security and privacy. Through case studies and illustrative examples, we’ll demonstrate the tangible benefits and provide a roadmap for successful implementation.
Defining Big Data and AI in Business Context

Big data and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming business operations, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency and growth. Understanding their individual characteristics and their synergistic potential is crucial for leveraging these technologies effectively. This section defines big data and AI within a business context, exploring their key features and illustrating their practical applications.
Big Data Characteristics in Business
Big data, in a business context, refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are difficult to process using traditional data processing applications. These datasets possess several key characteristics, often summarized as the “five Vs”: Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value. High volume implies massive datasets exceeding the capacity of typical databases. Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed.
Variety encompasses the diverse formats of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information. Veracity addresses the accuracy and reliability of the data, crucial for drawing meaningful insights. Finally, value represents the potential of the data to generate actionable business intelligence. These characteristics present both challenges and opportunities for businesses seeking to extract meaningful insights. For example, a large e-commerce company might generate terabytes of data daily from customer transactions, website activity, and social media interactions.
Analyzing this data in real-time (high velocity) to personalize recommendations (high value) requires robust big data processing infrastructure.
AI Algorithms Suitable for Big Data Integration
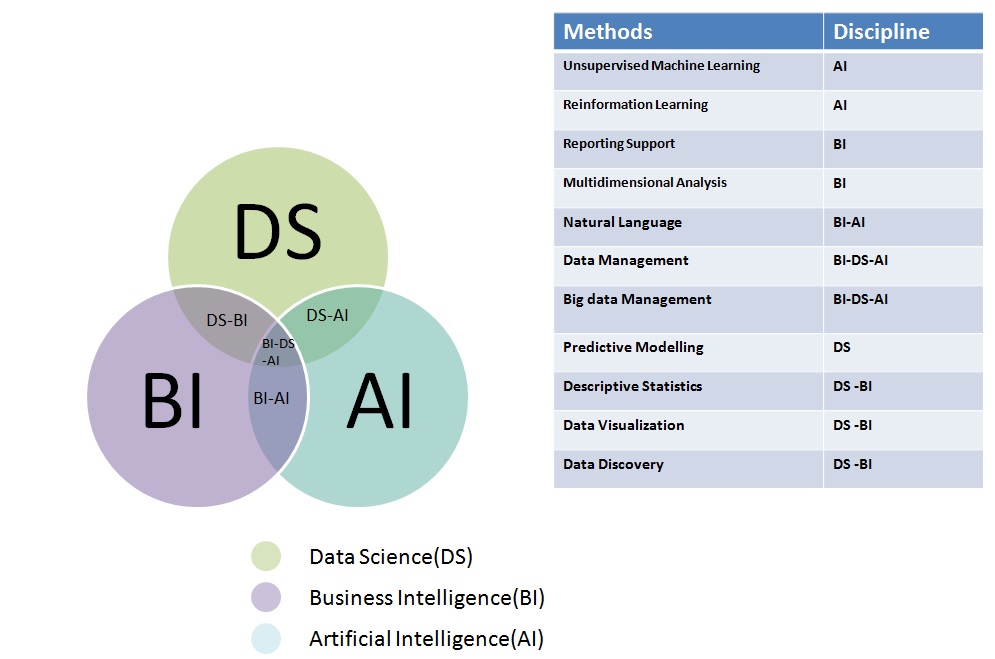
Several AI algorithms are particularly well-suited for processing and analyzing big data. Machine learning (ML), a subset of AI, plays a central role. Specific ML algorithms include: supervised learning (e.g., regression, classification) for predicting outcomes based on labeled data; unsupervised learning (e.g., clustering, dimensionality reduction) for identifying patterns and structures in unlabeled data; and reinforcement learning for training agents to make optimal decisions in dynamic environments.
Deep learning, a more advanced form of ML using artificial neural networks with multiple layers, excels in processing complex, high-dimensional data, such as images and text. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms are essential for analyzing textual data, extracting insights from customer reviews, social media posts, and other unstructured text sources. The choice of algorithm depends on the specific business problem and the nature of the available data.
For instance, a bank might use a classification algorithm to detect fraudulent transactions, while a retailer might employ clustering algorithms to segment customers based on purchasing behavior.
Examples of Big Data and AI Integration in Business
Numerous businesses are already leveraging the combined power of big data and AI. Netflix uses big data analytics and machine learning algorithms to personalize movie and TV show recommendations for its subscribers, leading to increased user engagement and subscription renewals. Amazon utilizes AI-powered systems to optimize its supply chain, predict demand, and personalize customer experiences through targeted advertising and product recommendations.
Financial institutions employ AI algorithms to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and provide personalized financial advice. Healthcare providers use AI to analyze patient data, predict disease outbreaks, and develop personalized treatment plans. These examples highlight the broad applicability of big data and AI across diverse industries.
Comparison of Traditional Business Intelligence and AI-Powered Big Data Analytics
| Feature | Traditional Business Intelligence | AI-Powered Big Data Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Structured, internal data | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data; internal and external sources |
| Analysis Methods | Descriptive and diagnostic analytics | Descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics |
| Insights Generated | Summarized reports and dashboards | Actionable insights, predictions, and automated decision-making |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable to handle massive datasets |
Integration Strategies and Architectures
Successfully integrating big data and AI requires a strategic approach that considers data flow, system compatibility, and scalability. The choice of integration strategy significantly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of the resulting system, determining factors like deployment speed, cost, and overall performance. Several key approaches exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Data Integration Approaches
Different approaches exist for integrating big data and AI systems. A common method is to establish a centralized data lake or warehouse where all relevant data is stored and processed before being fed into AI models. This approach offers a holistic view of the data but can be computationally intensive and require significant upfront investment. Alternatively, a federated approach allows AI models to access data from various sources without centralizing it.
This approach improves data security and reduces the processing load on a central system, but can be more complex to manage and requires careful coordination between different data sources. A hybrid approach, combining elements of both centralized and federated architectures, often provides the best balance between efficiency and manageability. The optimal approach depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
Improving Business Efficiency through AI-Powered Insights: Big Data And AI Integration For Improved Business Efficiency
The integration of big data and artificial intelligence (AI) offers businesses unprecedented opportunities to enhance operational efficiency and gain a competitive edge. By leveraging the vast amounts of data generated daily, organizations can unlock valuable insights that inform strategic decision-making, optimize processes, and ultimately, drive significant improvements in productivity and profitability. This section explores key business processes that benefit from this integration, the role of predictive analytics, and the comparative advantages over traditional methods.
AI-powered insights significantly improve business efficiency by automating tasks, identifying patterns humans might miss, and enabling proactive rather than reactive decision-making. This translates to cost savings, increased revenue, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Key Business Processes Improved by Big Data and AI
Several core business functions experience substantial improvements when big data and AI are integrated. These improvements stem from the ability to analyze vast datasets, identify trends, and predict future outcomes with greater accuracy than traditional methods allow. For instance, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and risk management all benefit significantly. Improved forecasting accuracy leads to optimized inventory levels, personalized customer experiences, and proactive mitigation of potential risks.
Predictive Analytics and Enhanced Decision-Making, Big data and AI integration for improved business efficiency
Predictive analytics, a key application of AI, uses historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes. This capability transforms decision-making from a reactive to a proactive approach. For example, in sales and marketing, predictive models can identify high-potential customers, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize pricing strategies, leading to increased conversion rates and higher ROI. In manufacturing, predictive maintenance models, analyzing sensor data from machinery, predict equipment failures, allowing for preventative maintenance and minimizing costly downtime.
The accuracy and speed of these predictions far surpass the capabilities of human analysts relying solely on historical data and intuition.
Efficiency Gains: AI-Powered Insights vs. Traditional Methods
The efficiency gains achieved through AI-powered insights often dwarf those of traditional methods. Traditional methods rely heavily on manual data analysis, which is time-consuming, prone to errors, and limited in scope. AI, on the other hand, can process massive datasets in real-time, identify subtle patterns, and generate actionable insights much faster and more accurately. For example, consider fraud detection.
Traditional methods might detect only a fraction of fraudulent transactions, while AI-powered systems can identify complex patterns indicative of fraud with significantly higher accuracy, reducing losses and improving operational efficiency. The difference is not just incremental; it’s often a quantum leap in effectiveness and speed.
Real-World Applications of Big Data and AI for Improved Operational Efficiency
Numerous real-world examples demonstrate the transformative power of big data and AI. Netflix, for instance, uses big data and AI to personalize movie recommendations, significantly improving user engagement and retention. This data-driven approach allows them to tailor their content offerings to individual preferences, leading to higher subscription rates and reduced churn. Similarly, Amazon utilizes AI-powered algorithms to optimize its supply chain, predicting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and streamlining logistics, resulting in faster delivery times and reduced costs.
These examples highlight how organizations across diverse industries are leveraging big data and AI to improve operational efficiency and gain a competitive advantage.
Case Studies
The successful integration of big data and AI requires careful planning, execution, and a deep understanding of the business context. Several companies have demonstrated the transformative power of this synergy, achieving significant improvements in efficiency and profitability. Examining these case studies provides valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls.
Netflix’s Personalized Recommendations System
Netflix, a global streaming giant, leverages big data and AI extensively to power its recommendation engine. The company collects vast amounts of data on user viewing habits, including watch history, ratings, time spent watching, and even the devices used. This data is then fed into sophisticated AI algorithms, primarily collaborative filtering and content-based filtering, to predict which shows and movies users are most likely to enjoy.
Initially, Netflix faced the challenge of processing and analyzing this massive dataset efficiently. They overcame this by investing heavily in their cloud infrastructure and developing highly scalable algorithms capable of handling petabytes of data. Furthermore, the accuracy of recommendations was initially hampered by the “cold start problem,” where new users or content lacked sufficient data for accurate predictions.
They addressed this by incorporating contextual information, such as genre preferences and actor popularity, into their algorithms.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Netflix’s Recommendation System
| KPI | Description | Measurement | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Percentage of users who click on a recommended title. | Number of clicks / Number of recommendations shown | Increase by 10% year-over-year |
| Watch Time | Total time users spend watching recommended content. | Sum of viewing durations for recommended titles | Increase by 15% year-over-year |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of subscribers who continue their subscription. | Number of retained subscribers / Total number of subscribers | Maintain above 85% |
| Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) | Average revenue generated per subscriber. | Total revenue / Total number of subscribers | Increase by 5% year-over-year |
Impact on Business Functions
The improved recommendation system significantly impacted various business functions at Netflix. Marketing benefited from more targeted campaigns, focusing on specific user segments identified through data analysis. Sales experienced growth due to increased engagement and customer retention. Operations benefited from streamlined content delivery and reduced customer support inquiries related to finding relevant content. The overall impact has been a substantial increase in customer satisfaction, engagement, and revenue.
Challenges and Future Trends
The integration of big data and AI, while promising significant improvements in business efficiency, presents a range of challenges and necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. Furthermore, rapidly evolving technologies are poised to reshape the landscape of this integration, impacting various business sectors in profound ways.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Implementing big data and AI systems necessitates the collection, storage, and processing of vast amounts of sensitive data. This raises significant concerns regarding data security and privacy. Breaches can lead to substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and regular security audits, are crucial to mitigate these risks. Furthermore, compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is paramount.
Failure to address these concerns can severely hinder the adoption and effective utilization of big data and AI initiatives.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Decision-Making
The use of AI in business decision-making raises several ethical concerns. Bias in algorithms, leading to discriminatory outcomes, is a major issue. For example, an AI system trained on biased data might unfairly deny loan applications from specific demographic groups. Transparency and explainability of AI models are also crucial for ensuring fairness and accountability. “Black box” AI systems, where the decision-making process is opaque, can lead to mistrust and difficulty in identifying and rectifying errors.
Establishing clear ethical guidelines and implementing mechanisms for oversight and accountability are vital to address these challenges.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Big Data and AI Integration
Several emerging technologies are poised to further enhance the integration of big data and AI. Edge computing, for instance, allows for data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring real-time analysis, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation. Quantum computing holds the potential to solve complex computational problems that are currently intractable for classical computers, enabling more sophisticated AI models and faster data analysis.
The development of more efficient and robust AI algorithms, such as those based on neuromorphic computing, will also play a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of big data and AI systems.
Future Impact on Various Business Sectors
The future impact of big data and AI integration will vary across different business sectors. In healthcare, AI-powered diagnostic tools and personalized medicine are expected to significantly improve patient outcomes. The retail sector will see further advancements in personalized recommendations, supply chain optimization, and fraud detection. Financial institutions will leverage AI for risk management, fraud prevention, and algorithmic trading.
Manufacturing will benefit from predictive maintenance and improved process optimization. These advancements are likely to lead to increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and the creation of new business models across a wide range of industries. For instance, Amazon’s use of AI in its recommendation engine has dramatically increased sales and customer engagement, demonstrating the transformative potential of this technology.
Similarly, the use of predictive maintenance in manufacturing plants has led to significant reductions in downtime and maintenance costs.
Illustrative Examples
Big data and AI integration isn’t just theoretical; it’s transforming businesses across sectors. The following examples showcase how these technologies, when combined effectively, lead to significant efficiency gains. Visualizing these scenarios helps to understand the impact on a practical level.
Supply Chain Optimization through Big Data and AI
Imagine a global retailer with thousands of SKUs, numerous suppliers, and a vast distribution network. Manually managing this complexity is near impossible. However, by integrating big data analytics with AI, they can achieve unprecedented levels of optimization. The process begins with collecting data from various sources: sales data, inventory levels, supplier performance, shipping times, weather patterns, and even social media sentiment regarding product demand.
This data is then fed into AI algorithms, specifically machine learning models, that can identify patterns and predict future demand with considerable accuracy. For instance, a predictive model might forecast a surge in demand for specific items due to an upcoming holiday or a weather event. This allows the retailer to proactively adjust inventory levels, optimize logistics routes, and even negotiate better terms with suppliers.
The resulting efficiency improvements include reduced inventory holding costs, minimized stockouts, faster delivery times, and ultimately, increased profitability. A visual representation would show a complex network diagram of the supply chain, with data flows highlighted, and AI algorithms acting as a central control system, dynamically adjusting the network based on real-time data and predictions. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover rate, order fulfillment time, and transportation costs would be displayed, showing the positive impact of the AI-powered system.
For example, a reduction in transportation costs by 15% and a 10% decrease in stockouts could be visually represented through bar graphs comparing before and after implementation.
Enhanced Customer Service through AI-Powered Chatbots and Predictive Analytics
Consider a large telecommunications company struggling with high call volumes and long wait times for customer support. Implementing AI-powered chatbots and predictive analytics can significantly alleviate this burden. Big data from customer interactions, including call logs, online chats, and social media mentions, is analyzed to identify common customer issues, pain points, and frequently asked questions. This data is then used to train AI chatbots capable of handling a large percentage of routine inquiries, providing instant responses and resolving issues autonomously.
Predictive analytics, meanwhile, can forecast potential customer churn based on factors like usage patterns, billing history, and customer sentiment. This allows the company to proactively reach out to at-risk customers, offering personalized solutions and preventing churn. A visual representation might show a flowchart illustrating the customer journey, with different touchpoints (website, chatbot, phone call) clearly depicted. The chatbot’s role in handling routine inquiries would be highlighted, along with the predictive analytics engine identifying at-risk customers and triggering proactive interventions.
KPIs such as customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), average handling time (AHT), and customer churn rate would be presented graphically, demonstrating the positive impact of the AI-powered customer service system. For instance, a 20% reduction in AHT and a 10% decrease in customer churn rate could be visualized through comparative charts.
Final Review

The integration of big data and AI represents a pivotal shift in how businesses operate, offering a pathway to unprecedented efficiency and competitive advantage. While challenges exist, the potential rewards are immense. By strategically leveraging these powerful technologies, organizations can unlock new levels of operational excellence, drive innovation, and ultimately, thrive in an increasingly data-driven world. The future of business efficiency is inextricably linked to the successful integration of big data and AI, and the journey towards realizing this potential is one filled with both opportunity and exciting possibilities.

