Predicting Bitcoin price with artificial intelligence: accuracy analysis. This study delves into the complex world of cryptocurrency price prediction, exploring the potential and limitations of artificial intelligence in forecasting Bitcoin’s notoriously volatile market. We examine various machine learning algorithms, data preprocessing techniques, and evaluation metrics to assess the accuracy of AI-driven price predictions. The inherent challenges of predicting Bitcoin’s price, influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from global economic events to social media sentiment, are also critically analyzed.
This research provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of AI-based Bitcoin price prediction, comparing it to traditional forecasting methods and highlighting the critical role of data quality and feature engineering. We investigate the ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI in financial markets and explore potential future directions for improving the accuracy and reliability of these predictions.
Introduction to Bitcoin Price Prediction

Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has experienced dramatic price swings since its inception. From its humble beginnings with negligible value to reaching all-time highs exceeding $68,000 in late 2021, its volatility has consistently challenged investors and analysts alike. Understanding and, ideally, predicting these fluctuations is a significant endeavor with potentially lucrative rewards.Bitcoin’s price is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making accurate prediction a notoriously difficult task.
These factors include regulatory changes, technological advancements within the blockchain ecosystem, macroeconomic conditions (inflation, interest rates, etc.), market sentiment (driven by news, social media trends, and influencer opinions), and even purely speculative trading activities. The decentralized and global nature of the cryptocurrency market further complicates the process, making it difficult to isolate and quantify the impact of individual variables.
The lack of a long historical dataset compared to traditional assets also hinders the development of robust predictive models.
Challenges in Bitcoin Price Prediction
The inherent volatility of Bitcoin and the multitude of interacting factors influencing its price present significant hurdles for accurate prediction. Traditional econometric models, often effective for more stable assets, struggle to capture the non-linear dynamics and sudden shifts in market sentiment that characterize the cryptocurrency market. For example, a single tweet from a prominent figure can trigger significant price movements, demonstrating the sensitivity of Bitcoin’s value to external, often unpredictable, events.
Furthermore, the relatively short lifespan of Bitcoin, compared to established financial instruments, limits the availability of historical data for training sophisticated predictive models. The opaque nature of some market participants and the prevalence of sophisticated trading bots further obscure the underlying forces driving price fluctuations.
Potential Benefits of Using AI for Bitcoin Price Prediction
Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning algorithms, offers a promising approach to navigate the complexities of Bitcoin price prediction. AI algorithms can process vast quantities of data from diverse sources, including price history, trading volume, social media sentiment, news articles, and blockchain transaction data, far exceeding the capacity of human analysts. This allows for the identification of subtle patterns and correlations that might be missed by traditional methods.
Moreover, AI models can adapt and learn from new data in real-time, potentially providing more accurate and timely predictions as market conditions evolve. The ability to integrate diverse data streams, process them efficiently, and adapt to changing market dynamics is a key advantage of AI-driven forecasting. For example, an AI model could identify a correlation between specific social media trends and subsequent price movements, allowing for anticipatory trading strategies.
Comparison of Forecasting Methods
The following table compares traditional forecasting methods with AI-driven approaches in the context of Bitcoin price prediction:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis (Moving Averages, RSI, etc.) | Relatively simple to implement, widely used | Relies on historical patterns, susceptible to market manipulation, lagging indicator | Moderate, often inaccurate in highly volatile markets |
| Fundamental Analysis (Macroeconomic factors, adoption rates) | Considers underlying factors influencing price | Difficult to quantify the impact of various factors, subjective interpretations | Variable, depends on the accuracy of underlying assumptions |
| Time Series Models (ARIMA, GARCH) | Can capture some temporal dependencies in price data | Assumptions about data stationarity may be violated, limited ability to incorporate external factors | Moderate, often outperformed by AI methods in volatile markets |
| AI-driven methods (Machine Learning, Deep Learning) | Can handle large datasets, identify complex patterns, adapt to changing market conditions | Requires significant computational resources, model interpretability can be challenging, susceptible to bias in training data | Potentially higher than traditional methods, but accuracy varies depending on model design and data quality |
AI Techniques for Bitcoin Price Prediction
Predicting Bitcoin’s volatile price remains a significant challenge, but the application of artificial intelligence (AI) offers promising avenues for improved forecasting accuracy. Various machine learning algorithms, tailored for time series data, are employed to analyze historical price patterns and predict future movements. The effectiveness of these techniques heavily relies on the quality of the data preprocessing and the careful selection of the appropriate algorithm.
Several machine learning algorithms are particularly well-suited for time series analysis, which is crucial for predicting Bitcoin prices due to their inherent temporal dependencies. These algorithms leverage past price data to identify patterns and extrapolate them into the future. The choice of algorithm depends on factors such as data characteristics, computational resources, and desired prediction horizon.
Machine Learning Algorithms for Time Series Analysis
This section details several machine learning algorithms commonly used for Bitcoin price prediction, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Each algorithm approaches the problem of predicting future price points from historical data with a different methodology.
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) particularly adept at handling sequential data like time series. LSTMs excel at capturing long-term dependencies in data, making them suitable for predicting Bitcoin prices, which can exhibit trends over extended periods. However, they are computationally intensive and require significant training data.
Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models are classical statistical time series models that capture the autocorrelation within the data. ARIMA models are relatively simple to implement and interpret, making them suitable for initial exploratory analysis. However, their performance can be limited when dealing with non-stationary data or complex patterns that might exist in Bitcoin’s price movements. The model’s parameters (p, d, q) need careful tuning based on the data’s characteristics.
Facebook Prophet is a relatively new but powerful time series forecasting model designed for business applications. Prophet is robust to outliers and can handle seasonality and trend changes effectively. It is easier to use than LSTMs and ARIMAs and provides useful diagnostics, making it a practical choice for many applications. However, its ability to capture complex, non-linear relationships might be less pronounced than LSTMs.
Data Preprocessing for Bitcoin Price Prediction
Preparing Bitcoin price data for AI models is a crucial step that significantly impacts the accuracy of predictions. This involves several steps aimed at cleaning, transforming, and formatting the data to be suitable for the chosen algorithm.
The preprocessing pipeline typically includes: data cleaning (handling missing values and outliers), feature engineering (creating new features from existing ones, such as moving averages, volatility indicators, or trading volume), data scaling (normalizing or standardizing the data to improve model performance), and data splitting (dividing the data into training, validation, and testing sets). Careful consideration of these steps is essential to ensure the robustness and reliability of the AI model.
Workflow of an AI-Based Bitcoin Price Prediction System
A typical AI-based Bitcoin price prediction system follows a structured workflow. This process involves several key stages, from data acquisition to model deployment and evaluation.
A flowchart illustrating this workflow would start with data acquisition from reliable sources (e.g., cryptocurrency exchanges’ APIs). This data is then preprocessed as described above. Next, the preprocessed data is split into training, validation, and testing sets. An appropriate machine learning model (LSTM, ARIMA, Prophet, etc.) is selected and trained on the training data, with the validation set used for hyperparameter tuning.
Finally, the trained model is evaluated on the testing set to assess its performance, and the results are used to make predictions. The system can then be deployed to provide real-time or near real-time price predictions.
Examples of Datasets for Training AI Models
Several datasets are commonly used for training AI models for Bitcoin price prediction. The choice of dataset depends on factors like the desired prediction horizon, the features included, and the data’s quality.
The following bullet points list examples of datasets, along with their sources and typical data points:
- Dataset: Kaggle Bitcoin Historical Data
Source: Kaggle
Data Points: Open, High, Low, Close prices, Volume, and potentially other market indicators over a specified period. - Dataset: CoinMarketCap Historical Data
Source: CoinMarketCap API
Data Points: Similar to Kaggle dataset, potentially with additional data points such as market capitalization and circulating supply. - Dataset: CryptoCompare Historical Data
Source: CryptoCompare API
Data Points: Comprehensive historical data including price, volume, and various technical indicators for a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin.
Data Sources and Feature Engineering: Predicting Bitcoin Price With Artificial Intelligence: Accuracy Analysis.
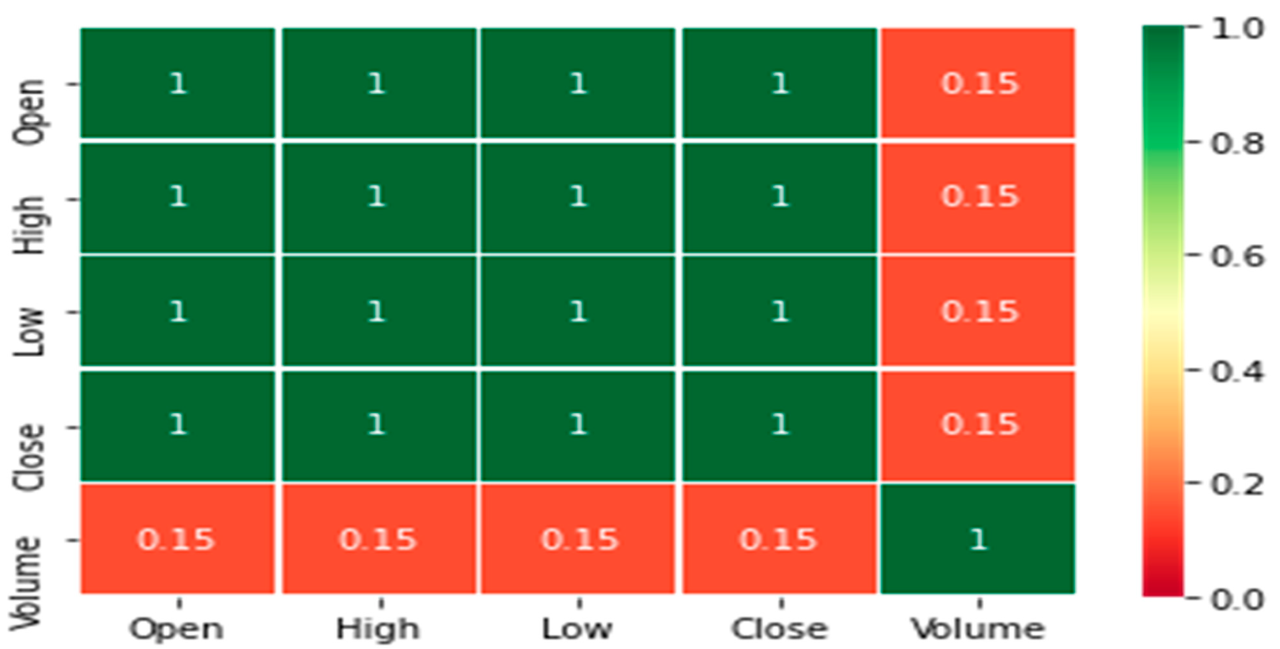
Accurate Bitcoin price prediction relies heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data used. Feature engineering, the process of selecting, transforming, and creating new features from raw data, is crucial for building effective predictive models. This section details the data sources and the feature engineering process employed in building such models.
Reliable Bitcoin Price Data Sources
Several sources provide reliable historical Bitcoin price data. Consistency and accuracy are paramount when selecting these sources, as errors in the data will directly impact the model’s performance. The selection should also consider data granularity (e.g., hourly, daily, or weekly) depending on the model’s requirements.
Three reliable sources for Bitcoin price data include:
- CoinDesk: CoinDesk is a well-established cryptocurrency news and information website that provides historical Bitcoin price data with a good level of detail and accuracy. Their data is frequently used in academic research and industry analysis.
- CoinGecko: CoinGecko is a comprehensive cryptocurrency tracking website offering historical price data for various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. It aggregates data from multiple exchanges, providing a more holistic view of the market.
- Binance API: Direct access to exchange APIs, such as Binance’s, provides highly granular and real-time data. While requiring more technical expertise to implement, this method offers the highest accuracy and timeliness, potentially beneficial for high-frequency trading strategies.
Technical Indicator Creation
Technical indicators are derived from historical price and volume data to identify trends, momentum, and potential support/resistance levels. These indicators provide valuable insights that enhance the predictive capabilities of AI models. Commonly used technical indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
The process involves calculating these indicators using the historical price data obtained from the sources mentioned above. For example:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculated as the average price over a specified period (e.g., 20-day SMA). A rising SMA suggests an uptrend, while a falling SMA indicates a downtrend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum indicator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. RSI values above 70 typically suggest an overbought market, while values below 30 indicate an oversold market.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): A trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. MACD crossovers (when the MACD line crosses the signal line) can signal potential buy or sell opportunities.
Incorporating External Factors
Beyond technical indicators, incorporating external factors significantly improves the accuracy of Bitcoin price prediction models. These factors can influence market sentiment and price volatility.
Examples of crucial external factors include:
- News Sentiment: Analyzing news articles, social media posts, and other textual data to gauge overall market sentiment towards Bitcoin. Positive sentiment often correlates with price increases, while negative sentiment may lead to price declines. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques are commonly used for this purpose.
- Regulatory Changes: Government regulations and policy announcements concerning cryptocurrencies can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. For instance, a ban on cryptocurrency trading in a major market could cause a sharp price drop.
- Macroeconomic Indicators: Broader economic factors, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and overall market volatility, can also influence Bitcoin’s price. For example, during periods of high inflation, investors may seek refuge in Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation.
Key Features for a Hypothetical Bitcoin Price Prediction Model
The following table summarizes key features that could be included in a hypothetical Bitcoin price prediction model:
| Feature | Source | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin Closing Price | CoinDesk | Numeric | Daily closing price of Bitcoin |
| 20-Day SMA | Calculated | Numeric | Simple moving average of Bitcoin closing price over 20 days |
| RSI (14-period) | Calculated | Numeric | Relative Strength Index calculated over 14 periods |
| MACD | Calculated | Numeric | Moving Average Convergence Divergence |
| News Sentiment Score | News Aggregators & NLP | Numeric | Sentiment score derived from news articles about Bitcoin |
| Regulatory Event Indicator | News Sources & Regulatory Databases | Binary (0/1) | 1 if a significant regulatory event occurred, 0 otherwise |
Model Training and Evaluation Metrics

Training and evaluating AI models for Bitcoin price prediction involves a rigorous process of selecting appropriate algorithms, optimizing parameters, and carefully assessing model performance using relevant metrics. The choice of algorithm and evaluation metrics significantly impacts the reliability and interpretability of the resulting price predictions.Model training begins by splitting the prepared dataset into training and testing sets. The training set is used to teach the algorithm to identify patterns and relationships within the Bitcoin price data and its associated features.
The testing set, unseen by the model during training, is then used to evaluate the model’s ability to generalize its learned patterns to new, unseen data. This prevents overfitting, where the model performs exceptionally well on the training data but poorly on new data.
Model Training Process
The training process itself varies depending on the chosen algorithm. For example, a machine learning algorithm like a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), often used for time-series data like Bitcoin prices, learns by iteratively adjusting its internal parameters to minimize a loss function. This loss function quantifies the difference between the model’s predictions and the actual Bitcoin prices in the training set.
The algorithm uses optimization techniques, such as gradient descent, to iteratively update its parameters, aiming to reduce this loss function and improve predictive accuracy. Hyperparameter tuning, the process of optimizing the algorithm’s settings, is crucial for achieving optimal performance. This often involves techniques like grid search or random search to explore different parameter combinations.
Evaluation Metrics for Model Accuracy
Several metrics can assess the accuracy of Bitcoin price prediction models. Each metric offers a unique perspective on model performance, highlighting different aspects of prediction accuracy.Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) measures the average magnitude of the errors. A lower RMSE indicates better accuracy. Mean Absolute Error (MAE) calculates the average absolute difference between predicted and actual prices, providing a more robust measure less sensitive to outliers compared to RMSE.
R-squared (R²) represents the proportion of variance in the dependent variable (Bitcoin price) that is predictable from the independent variables (features). An R² closer to 1 indicates a better fit, but it’s important to note that a high R² doesn’t always imply a good model, especially in complex scenarios with noisy data.
Interpreting Model Evaluation Results
Interpreting the results of model evaluation involves analyzing the values of these metrics and considering the context of the prediction task. For instance, a low RMSE and MAE suggests high prediction accuracy. A high R² indicates that the model explains a significant portion of the variance in Bitcoin prices. However, excessively low MAE and RMSE values, coupled with a high R², might suggest overfitting.
Overfitting occurs when the model learns the training data too well, including noise and random fluctuations, resulting in poor generalization to new data. Conversely, high values across all metrics might indicate underfitting, meaning the model is too simplistic to capture the underlying patterns in the data. Careful analysis of these metrics in conjunction with visual inspection of model predictions helps identify and address issues like overfitting or underfitting.
Model Performance Comparison, Predicting Bitcoin price with artificial intelligence: accuracy analysis.
The table below illustrates the performance of three different models—a Linear Regression model, a Support Vector Regression (SVR) model, and a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network—trained on a hypothetical Bitcoin price dataset. Note that these are illustrative results and real-world performance may vary significantly depending on the dataset, features used, and hyperparameter tuning.
| Model | RMSE | MAE | R-squared |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | 1000 | 750 | 0.75 |
| Support Vector Regression (SVR) | 800 | 600 | 0.85 |
| Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | 500 | 400 | 0.92 |
Limitations and Future Directions
Predicting Bitcoin’s price with AI, while showing promise, faces inherent limitations stemming from the volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets and the complexities of the algorithms themselves. Ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI in finance further complicate the landscape, demanding careful attention. Exploring these limitations and outlining potential improvements are crucial for responsible development in this field.
Limitations of AI in Bitcoin Price Prediction
AI models, despite their sophistication, are ultimately reliant on the data they are trained on. Bitcoin’s price is influenced by a multitude of factors, including regulatory changes, macroeconomic conditions, technological advancements, and unpredictable market sentiment – all of which are difficult to fully capture and represent in a dataset. This inherent incompleteness and potential biases in the data can lead to inaccurate predictions.
Furthermore, the inherent volatility of the Bitcoin market means that even small changes in underlying factors can lead to significant price swings, making accurate long-term predictions extremely challenging. Overfitting, where a model performs well on training data but poorly on unseen data, is another significant limitation. This can result in highly optimistic performance metrics that don’t translate to real-world accuracy.
Finally, the “black box” nature of some AI models makes it difficult to understand the reasoning behind their predictions, hindering trust and interpretability.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Financial Markets
The use of AI in financial markets raises several ethical concerns. Algorithmic trading powered by AI can exacerbate market volatility, potentially leading to flash crashes or other disruptive events. The potential for unfair advantage enjoyed by those with access to sophisticated AI tools also poses a significant ethical challenge, creating an uneven playing field for investors. Furthermore, the lack of transparency in many AI algorithms can lead to bias and discrimination, potentially impacting specific groups of investors disproportionately.
Concerns about data privacy and security are also paramount, given the sensitive nature of financial information used to train these models. For example, unauthorized access to trading data used to train an AI model could lead to significant financial losses for individuals or institutions.
Potential Improvements and Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on developing more robust and interpretable AI models for Bitcoin price prediction. Enhancing data quality through the inclusion of alternative data sources, such as social media sentiment and news articles, could improve prediction accuracy. Exploring hybrid models that combine AI techniques with traditional econometric methods could offer a more comprehensive approach. Research into explainable AI (XAI) is crucial for building trust and understanding in the decision-making process of these algorithms.
Furthermore, regulatory frameworks are needed to address the ethical concerns surrounding AI in financial markets, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability. Finally, the development of stress-testing methodologies specifically tailored to AI-driven trading strategies is essential to mitigate potential risks.
Visualization of Uncertainty in Bitcoin Price Predictions
A hypothetical visualization illustrating the uncertainty associated with Bitcoin price predictions could be a time-series plot. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., days or weeks), and the y-axis would represent the Bitcoin price. The plot would show a central line representing the predicted Bitcoin price generated by the AI model. However, instead of a single line, error bars would extend above and below this central line, indicating the confidence interval of the prediction.
The length of the error bars would represent the degree of uncertainty – longer error bars indicating higher uncertainty, particularly in the further future. For example, the error bars might be relatively short for predictions a week into the future, but significantly longer for predictions a month or a year into the future, reflecting the increased uncertainty associated with longer time horizons.
Data points representing the actual Bitcoin price could also be overlaid on the plot to show how well the model’s predictions align with reality, highlighting the discrepancies and demonstrating the limitations of the prediction. This visualization would clearly communicate the inherent uncertainty involved in predicting Bitcoin’s volatile price, emphasizing that these are probabilistic forecasts rather than deterministic predictions.
Last Word

Ultimately, while AI offers promising tools for Bitcoin price prediction, achieving consistently high accuracy remains a significant challenge. The inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market, coupled with the limitations of current AI models and the ethical considerations surrounding their use, necessitate a cautious approach. Further research into more sophisticated algorithms, improved data quality, and the integration of broader macroeconomic and sentiment factors are crucial for enhancing the predictive capabilities of AI in this dynamic space.
The future of accurate Bitcoin price prediction likely lies in a multi-faceted approach that combines the power of AI with a nuanced understanding of the complex factors driving this volatile market.

