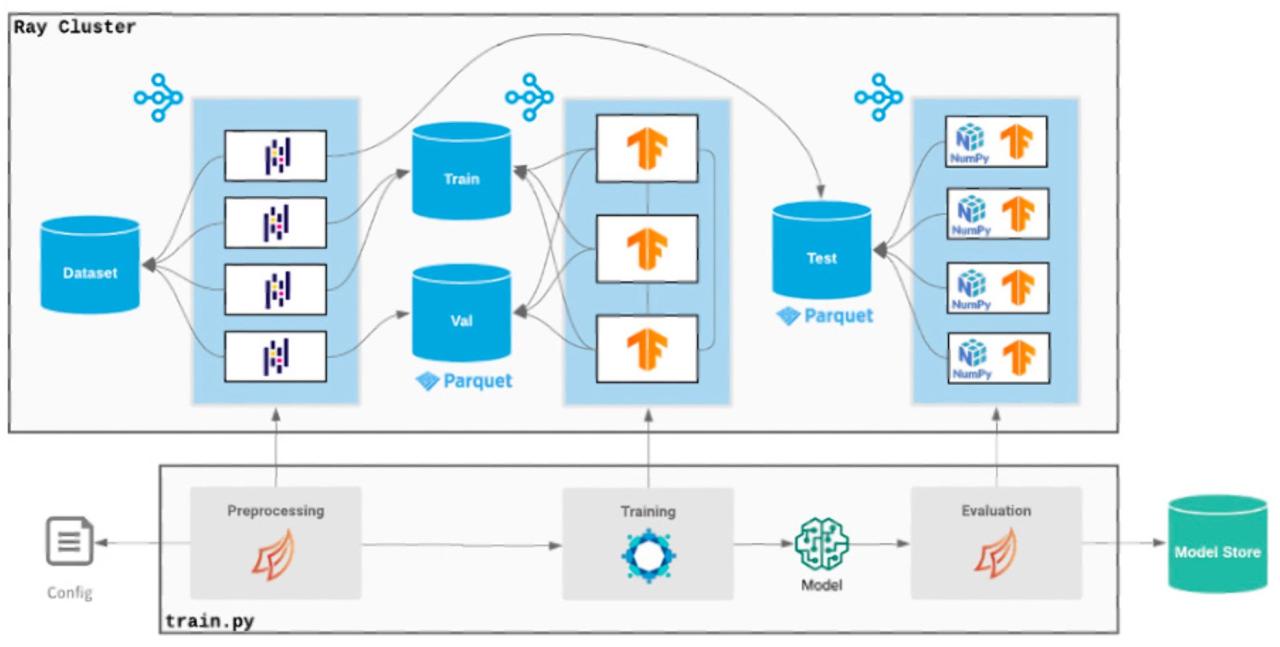
The role of AI in extracting insights from big data is revolutionizing how we understand and utilize the massive datasets generated daily. Traditional methods struggle to cope with the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of this data, leaving valuable information untapped. AI, however, with its advanced algorithms and processing power, offers a powerful solution, unlocking hidden patterns and predictions that would otherwise remain invisible.
This exploration delves into the various AI techniques employed, their applications across diverse industries, and the ethical considerations inherent in this transformative process.
From predicting disease outbreaks in healthcare to detecting financial fraud and personalizing marketing campaigns, AI’s impact is undeniable. We’ll examine specific examples, compare different AI algorithms like machine learning and deep learning, and discuss the critical role of natural language processing in analyzing unstructured data. Furthermore, we’ll address the challenges and ethical implications, including potential biases and data privacy concerns, offering insights into mitigating these risks and ensuring responsible AI implementation.
Introduction to AI and Big Data
The current era is characterized by an unprecedented explosion of data, encompassing diverse sources like social media interactions, sensor networks, and transactional databases. This deluge of information, often referred to as big data, presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. Effectively harnessing its potential requires sophisticated tools and techniques capable of handling its volume, velocity, variety, and veracity.Big data’s sheer scale surpasses the capabilities of traditional data analysis methods.
These methods, often relying on structured data and simpler analytical models, struggle to process the vast, complex, and often unstructured nature of big data. Limitations include processing time, computational resource constraints, and the inability to identify subtle patterns or correlations hidden within the massive datasets. Traditional approaches frequently fall short in providing timely and actionable insights, hindering informed decision-making across various sectors.
AI’s Role in Big Data Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), offers powerful solutions to the limitations of traditional data analysis when dealing with big data. AI algorithms are designed to automatically learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions without explicit programming. This capability is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from the complexity and volume inherent in big data.
For instance, ML algorithms can be trained to identify fraudulent transactions in real-time by analyzing vast amounts of transactional data, something impossible for manual review. Deep learning models, with their ability to process unstructured data like images and text, can be used to analyze social media sentiment, predict customer behavior, or even diagnose medical conditions from medical images with higher accuracy than traditional methods.
These AI techniques enable faster processing, improved accuracy, and the discovery of previously hidden correlations within big data.
Big Data Challenges and AI Solutions
The challenges associated with big data are multifaceted. Data volume necessitates efficient storage and processing solutions; data velocity demands real-time or near real-time analysis; data variety requires handling diverse data formats and structures; and data veracity necessitates dealing with inconsistencies and inaccuracies. AI addresses these challenges by providing scalable and efficient algorithms for data processing, real-time analytical capabilities, and robust methods for handling unstructured and semi-structured data.
Furthermore, AI techniques like anomaly detection can help identify and mitigate data quality issues, improving the overall veracity of insights derived from big data. For example, AI-powered systems can automatically flag inconsistencies or outliers in a dataset, prompting further investigation and improving the reliability of the analysis.
AI Techniques for Big Data Insight Extraction

The exponential growth of big data necessitates sophisticated analytical techniques to extract meaningful insights. Artificial intelligence (AI), encompassing machine learning and deep learning, provides a powerful arsenal of tools for this purpose. These techniques enable the discovery of patterns, predictions of future trends, and ultimately, data-driven decision-making across diverse industries. This section delves into specific AI algorithms and their applications in big data analysis.
Comparison of AI Algorithms for Big Data Analysis
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) are both subsets of AI, but they differ significantly in their approach and capabilities. ML algorithms learn from data using statistical methods, often requiring feature engineering—the manual selection and transformation of relevant data features. DL, a more advanced form of ML, uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to automatically learn features from raw data, requiring less manual intervention but demanding significantly more computational resources.
Both are crucial for big data analysis, with the choice depending on data characteristics and available resources.
Supervised Learning for Insight Extraction
Supervised learning algorithms learn from labeled data, where each data point is associated with a known outcome. This allows the algorithm to map inputs to outputs and make predictions on new, unseen data. For example, a supervised learning model can be trained on historical sales data (including features like price, promotions, and seasonality) to predict future sales. This allows businesses to optimize pricing strategies and inventory management.
Another example is fraud detection, where labeled data (fraudulent vs. non-fraudulent transactions) trains a model to identify suspicious activities.
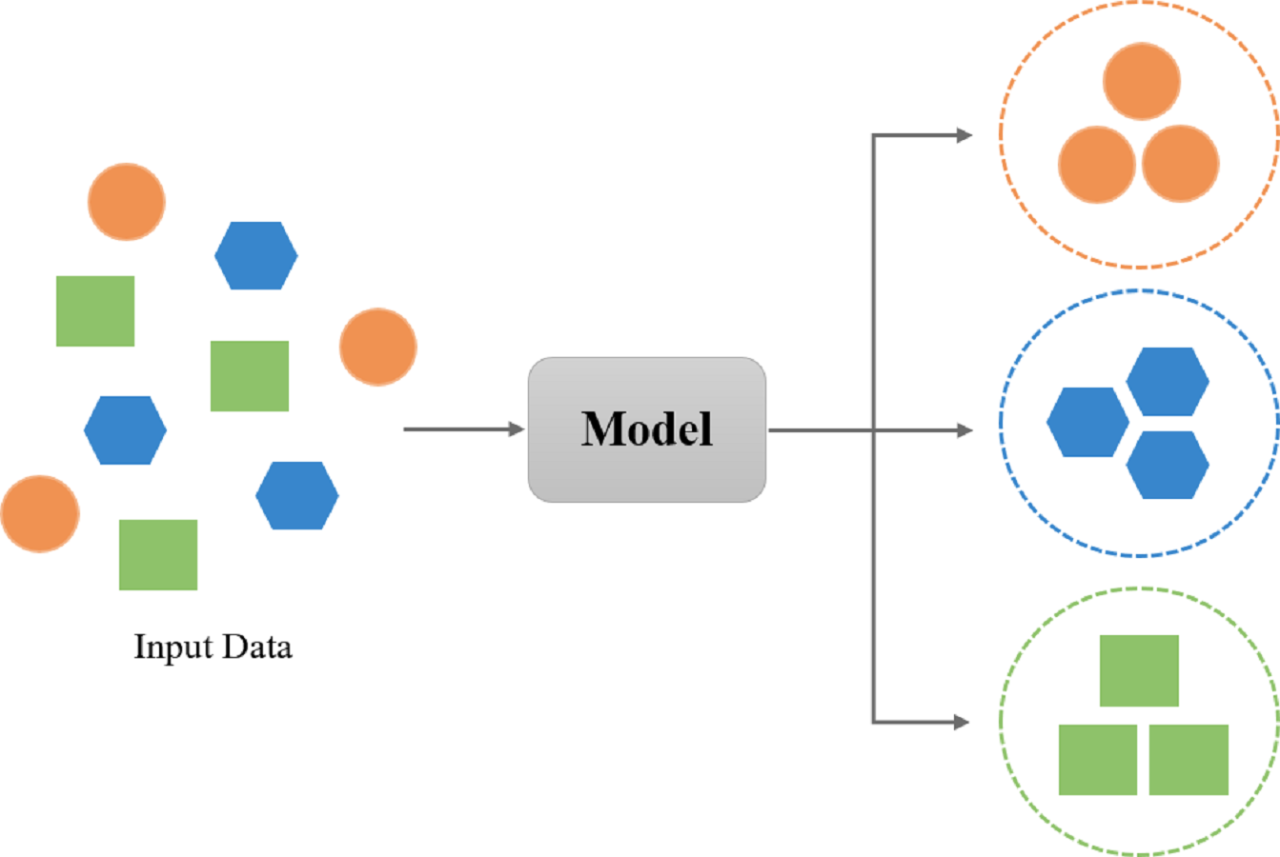
Unsupervised Learning for Insight Extraction
Unsupervised learning algorithms analyze unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns and structures. Clustering algorithms, such as k-means, group similar data points together, revealing underlying segments within the data. For instance, customer segmentation based on purchasing behavior can identify distinct customer groups with different needs and preferences, informing targeted marketing campaigns. Dimensionality reduction techniques, like principal component analysis (PCA), reduce the number of variables while preserving important information, simplifying data analysis and visualization.
For example, PCA can be used to analyze gene expression data, identifying key genes associated with a disease.
Reinforcement Learning for Insight Extraction
Reinforcement learning (RL) involves an agent learning to interact with an environment to maximize a reward. This is particularly useful in dynamic systems where the optimal strategy evolves over time. For example, RL can be used to optimize traffic flow in a smart city by adjusting traffic light timings based on real-time traffic data. Another application is in robotics, where RL algorithms enable robots to learn complex tasks through trial and error, maximizing efficiency and performance.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Textual Data Insight Extraction
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a crucial AI technique for extracting insights from textual big data. NLP algorithms enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This is vital for analyzing social media sentiment, customer reviews, news articles, and other unstructured textual data. Techniques like sentiment analysis gauge the emotional tone of text (positive, negative, or neutral), providing valuable feedback on brand perception or product reviews.
Topic modeling can identify recurring themes and topics within large text corpora, helping researchers understand trends and patterns in research publications or news articles.
| Algorithm | Strengths | Weaknesses | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Simple, interpretable, computationally efficient | Assumes linear relationship, sensitive to outliers | Predicting sales, stock prices |
| Logistic Regression | Simple, interpretable, efficient for binary classification | Assumes linear relationship, sensitive to outliers | Fraud detection, spam filtering |
| Decision Trees | Easy to understand, handles both categorical and numerical data | Prone to overfitting, can be unstable | Customer segmentation, risk assessment |
| Support Vector Machines (SVM) | Effective in high-dimensional spaces, versatile kernel functions | Can be computationally expensive for large datasets, choice of kernel is crucial | Image classification, text categorization |
| Neural Networks | Can model complex non-linear relationships, high accuracy | Computationally expensive, requires large datasets, can be difficult to interpret | Image recognition, natural language processing |
| K-Means Clustering | Simple, efficient for large datasets | Requires specifying the number of clusters, sensitive to initial conditions | Customer segmentation, anomaly detection |
Specific Applications of AI in Big Data Analysis Across Industries

The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics has revolutionized various sectors, enabling businesses to extract actionable insights previously unattainable. AI algorithms, trained on massive datasets, identify patterns, predict outcomes, and automate processes, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and decision-making across numerous industries. This section will explore specific applications of AI in big data analysis within healthcare, finance, and marketing, highlighting the transformative impact of this technological synergy.
AI’s ability to process and analyze complex, high-volume data allows for the identification of previously hidden correlations and trends, leading to more accurate predictions and informed strategic choices. This translates to tangible benefits such as improved patient care, enhanced risk management, and more effective marketing campaigns. The following examples illustrate the diverse applications and impactful results.
AI in Healthcare Big Data Analysis
AI is transforming healthcare by enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved drug discovery. Machine learning algorithms analyze patient medical records, genetic data, and lifestyle information to identify risk factors for specific diseases, predict disease outbreaks, and personalize treatment strategies. For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans) to detect anomalies with higher accuracy than human experts, leading to earlier and more effective interventions.
Predictive modeling can forecast patient readmission rates, enabling hospitals to proactively manage patient care and reduce healthcare costs. Furthermore, AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing vast amounts of genomic and chemical data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy.
AI in Financial Sector Big Data Analysis
The financial sector generates massive amounts of data daily, creating opportunities for AI-driven insights. AI algorithms are used extensively for fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. For instance, AI systems can analyze transaction patterns to identify anomalies indicative of fraudulent activity, significantly reducing financial losses. In risk management, AI models assess creditworthiness, predict loan defaults, and optimize investment portfolios by analyzing market trends and economic indicators.
Algorithmic trading leverages AI to execute trades at optimal prices, maximizing returns and minimizing risks. One example is the use of AI to detect insider trading by analyzing unusual trading patterns and communications data.
AI in Marketing and Advertising Big Data Analysis
AI is revolutionizing marketing and advertising by enabling highly targeted campaigns, personalized customer experiences, and improved campaign performance measurement. AI algorithms analyze customer data, including demographics, purchase history, browsing behavior, and social media activity, to segment customers into distinct groups with similar needs and preferences. This allows marketers to tailor their messaging and offers to specific segments, increasing conversion rates and customer engagement.
For example, AI-powered recommendation engines personalize product suggestions for online shoppers, leading to increased sales. Furthermore, AI optimizes advertising campaigns by analyzing real-time data to adjust bidding strategies and target audiences, maximizing the return on advertising spend. Predictive analytics can forecast customer churn, enabling businesses to proactively engage at-risk customers and improve customer retention.
- Industry: Healthcare; Application: Disease prediction using patient data; Insight: Improved early detection and preventative care.
- Industry: Finance; Application: Fraud detection using transaction data; Insight: Reduced financial losses and improved security.
- Industry: Marketing; Application: Customer segmentation using behavioral data; Insight: Personalized marketing campaigns and increased conversion rates.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The application of AI to extract insights from big data, while offering transformative potential, presents significant challenges and ethical considerations that demand careful attention. These challenges span technical limitations, societal impacts, and the inherent biases embedded within both the data and the algorithms themselves. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring responsible and beneficial AI deployment.
Bias in AI Algorithms and Their Impact on Insights
AI algorithms learn from the data they are trained on. If this data reflects existing societal biases – for example, gender bias in hiring practices or racial bias in loan applications – the resulting AI model will likely perpetuate and even amplify these biases. This can lead to inaccurate, unfair, or discriminatory insights. For instance, an AI system trained on biased crime data might incorrectly predict higher crime rates in certain neighborhoods, leading to disproportionate policing and resource allocation.
The impact is a distortion of reality, perpetuating inequalities and undermining trust in AI-driven decision-making. Mitigating this requires careful data curation, algorithm design that incorporates fairness constraints, and ongoing monitoring for bias in model outputs.
Data Privacy and Security in AI-Driven Big Data Analysis
The use of AI in big data analysis often involves processing vast amounts of sensitive personal information. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure is paramount. Data breaches can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques, are crucial. Furthermore, compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is essential.
Failure to adequately address privacy and security concerns can erode public trust and hinder the adoption of AI-driven big data solutions.
Challenges Related to Data Interpretation and Misinterpretation of AI-Generated Insights
AI-generated insights are not inherently infallible. The complexity of AI models can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions, leading to a phenomenon known as the “black box” problem. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to identify and correct errors or biases in the insights. Furthermore, the sheer volume and complexity of big data can overwhelm human analysts, leading to misinterpretations or an overreliance on AI-generated conclusions without sufficient critical evaluation.
Therefore, a human-in-the-loop approach, combining AI capabilities with human expertise and judgment, is vital for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of insights.
Hypothetical Scenario: Ethical Implications and Mitigation, The role of AI in extracting insights from big data
Imagine a healthcare provider using AI to analyze patient data to predict the likelihood of readmission. The AI model, trained on historical data, identifies a correlation between readmission rates and socioeconomic status. This could lead to a misinterpretation that patients from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are inherently less compliant with treatment plans, leading to resource allocation biases. This is ethically problematic as it ignores other factors such as access to healthcare, quality of care, and social determinants of health.To mitigate this, a multi-pronged approach is needed: First, the AI model should be retrained to account for confounding variables, such as access to healthcare resources and social support systems.
Second, the insights generated by the AI should be reviewed by a team of clinicians and ethicists to ensure they are not perpetuating existing inequalities. Third, transparency is crucial; patients should be informed about how their data is being used and the potential limitations of the AI predictions. Finally, the system should be designed to flag potential biases and alert human reviewers to further investigation.
By incorporating these steps, the ethical risks associated with using AI for big data analysis in healthcare can be significantly reduced, ensuring that the technology serves to improve patient outcomes equitably.
Future Trends and Developments
The intersection of artificial intelligence and big data analysis is poised for explosive growth in the coming decade. This growth will be driven by advancements in algorithmic capabilities, increased computational power, and the ever-expanding volume of data generated across various sectors. Understanding these future trends is crucial for businesses and researchers alike to effectively leverage the power of AI for insightful decision-making.The future of AI in big data analysis hinges on several key developments, promising more efficient and insightful processes.
These developments will reshape how businesses approach data analysis, leading to more accurate predictions, better resource allocation, and more effective strategies.
Advancements in AI Algorithms and Their Impact on Insight Extraction
The development of more sophisticated AI algorithms will significantly enhance insight extraction from big data. For instance, advancements in deep learning architectures, such as transformers and graph neural networks, are already improving the accuracy of natural language processing (NLP) and anomaly detection. We can expect to see further refinement in these areas, leading to more nuanced understanding of complex datasets.
Furthermore, the rise of explainable AI (XAI) will be crucial, enabling greater transparency and trust in AI-driven insights. This will allow businesses to understandwhy* an AI system reached a particular conclusion, rather than simply accepting the output as a black box. For example, improved XAI could allow financial institutions to better understand why a fraud detection system flagged a particular transaction, leading to more effective fraud prevention strategies.
Similarly, advancements in federated learning will enable AI models to be trained on decentralized datasets, protecting sensitive information while still benefiting from the collective data pool.
The Evolving Role of Human Experts in Collaboration with AI in Big Data Analysis
While AI will automate many aspects of big data analysis, the role of human experts will remain vital. Instead of being replaced, human analysts will increasingly work
in collaboration* with AI systems. This collaborative approach will leverage the strengths of both
AI’s speed and computational power for processing vast datasets, and human expertise for critical thinking, contextual understanding, and ethical considerations. For example, a human data scientist might use AI to identify patterns in customer behavior, but then apply their domain expertise to interpret those patterns and develop targeted marketing campaigns. The human element will be crucial in validating AI-generated insights, ensuring accuracy, and addressing potential biases.
The future will likely see a shift towards a more human-in-the-loop approach, where humans actively guide and refine the AI’s analysis process.
Projected Growth of AI’s Role in Big Data Analysis
A visual representation of the projected growth could be depicted as an upward-sloping curve on a graph. The X-axis represents time (over the next 5-10 years), and the Y-axis represents the percentage of big data analysis tasks performed with AI assistance. The curve would start at a relatively low point, reflecting the current state, and then steadily increase at an accelerating rate.
This acceleration would be particularly noticeable in the later years, indicating the rapid adoption of AI-driven solutions across various industries. Specific data points could be included, for instance, showing a projected increase from 20% AI involvement in 2024 to 60% by 2029, reflecting a significant shift in the reliance on AI for data analysis. The graph could be further segmented by industry (e.g., finance, healthcare, retail) to illustrate varying rates of adoption based on factors like data maturity and regulatory landscapes.
This would visually represent the anticipated transformative impact of AI on big data analysis in the near future. For example, the healthcare sector, with its vast amounts of patient data, is expected to see rapid adoption of AI for personalized medicine and improved diagnostics, driving a steeper segment of the growth curve compared to industries with less readily available data.
End of Discussion: The Role Of AI In Extracting Insights From Big Data

In conclusion, the integration of AI in big data analysis represents a significant leap forward in our ability to derive actionable insights. While challenges remain, particularly regarding ethical considerations and algorithmic bias, the potential benefits across various sectors are immense. The future likely holds even more sophisticated AI algorithms and a closer collaboration between human experts and AI systems, paving the way for more accurate, efficient, and responsible data-driven decision-making.
The journey towards unlocking the full potential of big data with AI is ongoing, but the progress made so far is undeniably transformative.

